Ⅰ. 서 론
돌발성 난청은 순음청력검사상 3개 이상의 연속된 주파수에서 30 ㏈ 이상의 청력손실이 72시간 이내에 발생하는 감각 신경성 난청을 말하며, 이명, 이충만감, 어지럼증, 자성강청 등 여러 동반 증상을 가지는 것을 특징으로 한다1).
돌발성 난청은 10만 명당 5-27명 정도로 드물게 나타나는 질환이나 의료 접근성 부족, 빠른 회복 등을 이유로 병원에 내원하지 않을 가능성도 있어 유병률이 더 높을 수 있다2). 또한 최근 연구에 따르면 고령화, 생활습관 변화 등의 이유로 유병률이 증가하는 추세로 치료에 대한 중요성이 대두되고 있다3). 돌발성 난청은 조기 진단과 신속한 치료가 예후에 큰 영향을 미치므로, 임상적 특성과 치료를 체계적으로 분석하는 것이 중요하다4).
돌발성 난청의 원인은 대부분 미상이며, 바이러스 등의 감염, 외상, 혈관 혹은 혈액성 질환, 내이 또는 뇌의 구조 이상 등이 원인으로 제기되고 있다5).
돌발성 난청의 치료는 전신 스테로이드 요법이 일차적으로 고려되고, 전신 스테로이드 요법의 치료 반응이 부족할 경우 고실 내 스테로이드 요법, 고압산소요법을 고려한다. 그러나 스테로이드 요법은 혈당 증가, 쿠싱 증후군, 고관절 무혈성 괴사 등의 부작용이 있을 수 있고, 치료 시기를 놓칠 경우 약효가 현저히 떨어질 수 있다는 단점이 있다6).
돌발성 난청과 난청에 동반되는 이명은 의사소통 및 생활의 불편함을 불러일으키기 때문에 회복되지 않은 청력과 지속적인 이명은 심리적 스트레스를 유발할 수 있다. 이에 대체 혹은 보조 치료로서 한의 치료의 필요성이 강조된다.
돌발성 난청의 침 치료에 대한 국내외 선행 연구를 살펴보면, 침 치료에 대해 분석한 김 등7)의 연구가 보고되었고, 최근에는 돌발성 난청에 대한 침 치료의 유효성을 평가한 체계적 문헌 고찰과 메타분석이 보고된 바 있다8). 이를 통해 침 치료가 돌발성 난청에 유효하다는 점이 학계에서 제시되고 있다.
그러나 실제 임상 현장의 다양한 증례들을 분석하여 침 치료의 적용 범위와 임상적 특징을 구체화한 연구는 상대적으로 부족하다. 이에 본 연구에서는 국내외에서 발표된 증례들을 분석함으로써 돌발성 난청에 대한 침 치료의 실제 임상 활용을 구체화하고 한계를 파악하여 향후 임상 및 연구에서의 적용 가능성을 탐색하고자 하였다.
Ⅱ. 대상 및 방법
본 연구에서는 돌발성 난청의 침 치료에 대한 최근 국내외 연구 동향을 살펴보기 위해, 전통의학정보포털(Oriental medicine Advanced Searching Integrated System, OASIS), Pubmed, CNKI (China National Knowledge Infrastructure)에서 관련 논문을 검색하였다. 검색일은 2025년 5월 14일이며 대상 기간은 2018년 1월부터 2025년 5월까지로 설정하였다. 전통의학정보포털에서는 검색어로 ‘돌발성 난청’을 사용하였고 Pubmed, CNKI에서는 검색어로 ‘sudden hearing loss’, ‘sudden deafness’, ‘acupuncture’, ‘case’, ‘case report’, ‘case series’를 조합하여 사용하였다.
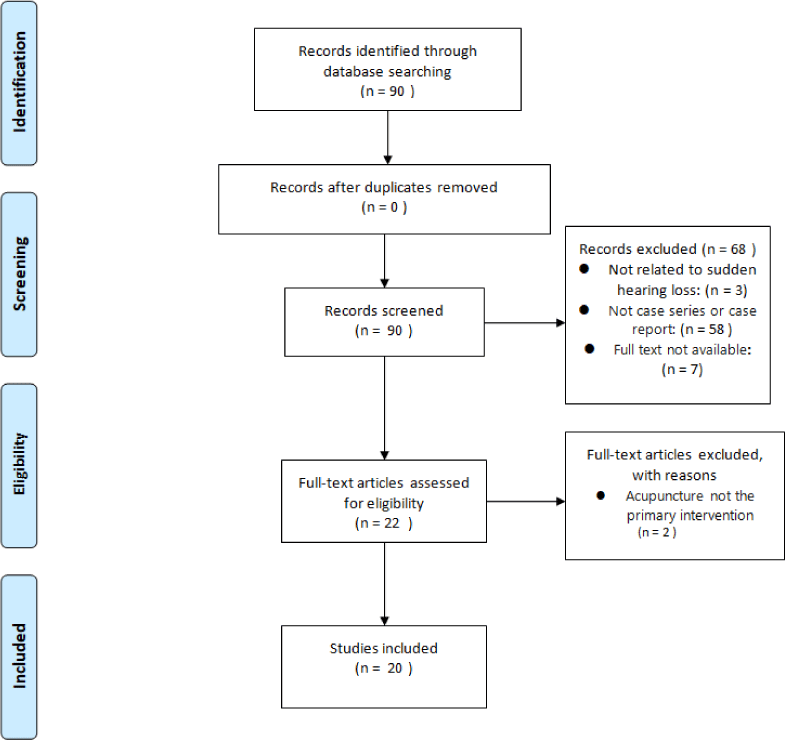
3개의 데이터베이스 검색 결과 Pubmed 50편, OASIS 12편, CNKI 28편 총 90편의 논문이 검색되었다. 이 중 중복되는 0편을 제외한 후 연구의 초록을 확인하여 돌발성 난청과 관련 없는 3편, 증례 보고나 증례군 연구가 아닌 58편, 원문이 제공되지 않는 논문 7편을 제외하고, 침 치료가 주된 중재가 아닌 2편을 제외하고 최종적으로 20편을 분석 대상 연구로 선택하였다(Fig. 1).
본 연구의 대상인 20편의 논문들을 분석하여 최근 시행되고 있는 연구의 논문 특성 (출판년도, 평가지표, 증례 수, 이상반응 보고), 대상 환자의 특성 (성별,연령, 일측성/양측성 여부, 동반 증상, 한의 치료 전 양방치료, 발병-치료 개시 기간)을 표로 정리하고, 치료 특성 (병행치료, 침의 규격, 유침시간, 치료 기간 및 빈도, 효과 분석, 치료의 세부사항)에 관한 정보를 다른 표로 정리하였다. 증례군 연구의 경우 치료 특성 등 각 례에서 공통적인 항목은 1편으로 서술하였고, 환자 특성 등 개별적인 항목은 1례로 서술하였다. 위와 같은 방법으로 침 치료를 중심으로 하여 돌발성 난청의 한의 복합 치료를 분석하였다.
Ⅲ. 결 과
국내 저널에 발표된 논문은 총 8편으로, 2019년 1편9), 2021년 1편10), 2022년 3편11-13), 2023년 1편14), 2024년 2편15,16)으로 조사되었다. 국외 저널에 발표된 논문은 총 12편으로 2018년 3편17-19), 2019년 2편20,21), 2020년 1편22), 2021년 1편23), 2023년 2편24,25), 2024년 3편26-28)으로 조사되었다.
돌발성 난청에 대한 침 치료의 유효성을 평가하기 위한 지표로 객관적 지표, 주관적 지표가 활용되었다. 객관적 지표로 순음청력검사(pure tone audiometry, PTA)를 사용한 연구는 17편으로 가장 많았다. 어음인지역치검사 (Speech Reception Threshold, SRT), 단어인지도검사(Word Recognition Score, WRS)는 4편, 변조 이음향방사 (Distortion-product OtoAcoustic Emission, DPOAE), 음소 균형 점수 (phonetically balanced score, PB score), 어음쾌적역치(Most Comfortable Loudness level, MCL), 최소차폐역치 검사(Minimal masking level, MML)는 1편에서 사용되었다.
주관적 지표로는 환자의 주관적 진술 13편, 이명 장애 지수 (Tinnitus Handicap Inventory, THI) 3편, NRS(Numeric Rating Scale) 1편에서 사용되었다.
20편 중 3편에서 이상반응이 없었다고 보고하였으며, 나머지 17편에서는 이상반응에 대해 명시하지 않았다(Table 1).
| First Author (Year) | Outcome Measures | Number of Patients | Adverse Event |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kim SY (2019)9) | §PTA, Subjective complaints | 3 | ††N.R |
| Kang YJ (2021)10) | PTA, §§SRT, ¶¶WRS, **MCL,¶THI, Subjective complaints | 1 | N.R |
| Lee JW (2022)11) | PTA, WRS, *DPOAE, Subjective complaints | 3 | N.R |
| Park SY (2022)12) | PTA, Subjective complaints | 1 | N.R |
| Seo JI (2022)13) | PTA, SRT WRS, THI, ‡NRS | 1 | N.R |
| Choi JW (2023)14) | PTA, SRT, †MML | 1 | N.R |
| Jung JW (2024)15) | PTA, Subjective complaints | 2 | N.R |
| Kim SJ (2024)16) | PTA, Subjective complaints | 1 | N.R |
| Zhong Y (2018)17) | Subjective complaints | 1 | N.R |
| He J (2018)18) | PTA, Subjective complaints | 1 | N.R |
| Kim MH (2018)19) | PTA, SRT, WRS | 1 | None |
| Arpornchayanon W (2019)20) | PTA, ‡‡PB score | 2 | None |
| Chen A (2019)21) | PTA | 1 | N.R |
| You C (2019)22) | PTA | 1 | N.R |
| LI J (2021)23) | Subjective complaints | 1 | N.R |
| Liu Y (2023)24) | PTA, Subjective complaints | 1 | N.R |
| Wang X (2023)25) | PTA, Subjective complaints | 1 | N.R |
| Zhang J (2024)26) | PTA, THI | 1 | None |
| Zhao F (2024)27) | Subjective complaints | 1 | N.R |
| Zhang Q (2024)28) | PTA, Subjective complaints | 1 | N.R |
연령대별로 40대 6례, 50대 6례로 40, 50대가 가장 많았고, 60대 5례, 30대 4례, 20대 3례, 15세 1례, 6세 1례 순으로 있었다.
성별은 여성 13례, 남성 13례가 있었다.
가장 많이 호소한 증상은 이명이며, 25례에서 호소하였고 나머지 1례에서는 호소하지 않았다.
이충만감은 10례, 어지럼증 6례, 자성강청 3례, 두통 2례, 경추 뻣뻣함 1례, 피로감 1례, 청각과민 1례, 귀 저림 1례, 현훈 1례 순으로 호소하였다.
경구 스테로이드 복용이 14례로 가장 많았다. 고실 내 스테로이드 주사요법은 10례, 비타민 B12 복용 및 주사, 말초 혈액 순환 개선제 복용 4례 어지럼증 치료제, 고압 산소 치료 2례, 혼합 가스 치료, 항바이러스 치료 1례가 있었다.
양방 치료의 경우 증상 발생 후 7일 이내에 치료 시작한 경우가 11례로 가장 많았다. 양방 치료 개시 기간이 약 1달인 경우 1례, 약 2달인 경우 1례 약 3달인 경우 1례 약 7달인 경우 1례가 있었다. 3례는 양방 치료를 시행하지 않았다. 나머지 8례는 양방 치료 개시 기간이 명시되지 않았다.
한의 치료의 경우 증상 발생 후 7일 이내에 치료를 시작한 경우가 7례, 7일 이후부터 1개월 이내로 치료를 시작한 경우 9례, 1개월 이후 치료를 시작한 경우 10례로 다양하였다(Table 2).
| First Author (Year) | Age, Sex | Laterality | Symptom Details | Western Medical Treatment Specifications | Onset-to-Treatment Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Western | Oriental | |||||
| Kim SY (2019)9) | 61/F | unilateral (left) | tinnitus, dizziness, headache | *IT steroid injections (5 times), Oral steroids and vasodilators (15 days) | 2 days | 18 days |
| 55/M | unilateral (right) | tinnitus, earfullness | None | None | 3 days | |
| 27/M | unilateral (left) | tinnitus, earfullness, fatigue | IT steroid injections (6 times) Oral steroids (13 days) | 1 day | 1 day | |
| Kang YJ (2021)10) | 36/M | unilateral (right) | tinnitus | None | None | 12 days |
| Lee JW (2022)11) | 36/F | unilateral (right) | tinnitus, earfullness, autophony | Oral steroids | 3 days | 12 days |
| 55/M | unilateral (right) | tinnitus, earfullness | Oral steroids | 3 days | 6 days | |
| 56/M | unilateral (left) | tinnitus, earfullness | IT steroid injections, Oral steroids | 30 days | 6 months | |
| Park SY (2022)12) | 33/F | bilateral | tinnitus | Oral steroids | †N.R | 9 months |
| Seo JI (2022)13) | 61/M | unilateral (right) | tinnitus | IT steroid injections, Vasodilators, Psychotropics, Gas therapy | 4 days | 11 days |
| Choi JW (2023)14) | 47/F | unilateral (left) | tinnitus | Oral steroids (2 months), Steroid injections, Hyperbaric oxygen therapy | N.R | 3 years |
| Jung JW (2024)15) | 54/F | unilateral (right) | tinnitus, earfullness | IT steroid injections (10 times) | 3 days | 44 days |
| 58/M | unilateral (left) | tinnitus, earfullness, autophony | IT steroid injections (10 times), Oral steroids | N.R | 62 days | |
| Kim SJ (2024)16) | 61/F | unilateral (right) | tinnitus, earfullness, hyperacusis, autophony | Oral steroids | 3 days | 9 days |
| Zhong Y (2018)17) | 26/M | unilateral (right) | tinnitus, dizziness | Oral Vasodilators | N.R | 10 days |
| He J (2018)18) | 49/M | unilateral (right) | tinnitus, dizziness, ear numbness | Antiviral therapy | 2 days | 6 days |
| Kim MH (2018)19) | 15/F | unilateral (left) | tinnitus | IT steroid injections (42 days) | 93 days | 8 months |
| Arpornchayanon W (2019)20) | 44/F | unilateral (right) | tinnitus, dizziness, vertigo | High-dose steroids,betahistine, Methylcobalamin (14 days) | 7 days | 6 month |
| 55/F | unilateral (right) | tinnitus, dizziness | High-dose steroids, Betahistine, Methylcobalamin (14 days) | 7 months | 6 year | |
| Chen A (2019)21) | 62/F | unilateral (right) | tinnitus, earfullness, dizziness | IT steroid injections (7 times) | N.R | 15 months |
| You C (2019)22) | 36/M | unilateral (left) | tinnitus, earfullness, headache | None | 7 days | 7 days |
| LI J (2021)23) | 43/F | unilateral (left) | tinnitus | Neurotrophic, Vasodilators | N.R | 14 days |
| Liu Y (2023)24) | 47/F | unilateral (left) | tinnitus, | IT steroid injections, Oral steroids | N.R | 7 days |
| Wang X (2023)25) | 24/F | unilateral (left) | tinnitus, | None | none | 5 days |
| Zhang J (2024)26) | 49/M | unilateral (left) | tinnitus, neck stiffness | Methylcobalamin, Postauricular drug injection, Oral steroids, Hyperbaric oxygen therapy | N.R | 15 days |
| Zhao F (2024)27) | 6/M | unilateral (left) | none | Oral steroids | 2 months | 2 months |
| Zhang Q (2024)28) | 62/M | unilateral (right) | tinnitus | Vasodilators, Vitamin B12 §IV injection | 1 day | 21 days |
뜸 치료는 11편으로 가장 많이 병행되었으며 전기 뜸 치료, 직접애주구, 간접애주구 등 다양하게 사용되었다.
전침은 6편에서 시행되었으며 4편에서는 2 ㎐, 3 ㎐의 저빈도 자극, 1편에서는 30 ㎐의 중빈도 자극, 1편에서는 전기 및 자기장 복합 침 자극이 가능한 의료기기를 사용하여 빈도수가 명시되지 않았다. 聽宮(SI19), 耳門(TE21), 翳風(TE17), 完骨(GB12)등의 이개 부위 혈자리가 사용되었다. 전침 자극 강도는 3편에서 환자가 견딜 수 있는 강도 또는 환자가 편하게 느낄 수 있는 정도로 시행되었고, 3편에서는 전침 자극 강도가 명시되지 않았다(Table 3).
| First author (year) | Treatment | Acupuncture Specification | Acupuncture Retention Time | Treatment Duration and Frequency | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kim SY (2019)9) | *A-tx, Moxibustion, Steam therapy, †H-med, ‣‣W-med (Oxicam,peripheral vasodilators), ***EA-tx | 0.20 ㎜×30 ㎜ | 20 minutes | admitted 17 days 2 times per day | §§PTA: improved from 57.5 ㏈ to 22.5 ㏈. Dizziness and headache resolved, Tinnitus reduced by 80% |
| admitted 8 days 2 times per day | PTA: improved from 75 ㏈ to 25 ㏈. Tinnitus reduced by 90%, Earfullness resolved. |
||||
| admitted 18 days 2 times per day | PTA: improved from 75 ㏈ to 20 ㏈. Tinnitus resolved, earfullness improved by 90%, Fatigue improved by 40%. |
||||
| Kang YJ (2021)10) | A-Tx, Moxibustion, H-med | 0.30 ㎜×40 ㎜ | 10 minutes | 60 days 1-2 times per week | PTA: improved from 50 ㏈ to 12.5 ㏈. ¶¶THI score: improved from 40 to 0, §§§SRT: improved from no response to 8 ㏈, ¶¶¶WRS: improved from 18% to 84%, †††MCL: decreased from 82 ㏈ to 48 ㏈. |
| Lee JW (2022)11) | A-Tx, Moxibustion, Dry cupping, §PA-Tx, ††Laser-Tx, W-med (peripheral vasodilators, corticosteroids) | 0.25 ㎜×40 ㎜ | 15 minutes | 8 days | PTA: improved from 16 ㏈ to 15 ㏈. 250 ㎐ threshold improved from 30 ㏈ to 15 ㏈. **DPOAE: increased from 14.7 to 16.5 ㏈ SPL WRS: improved from 96% to 100%. Tinnitus, autophony, and earfullness resolved. |
| 28 days | PTA: improved from 64 ㏈ to 18 ㏈. DPOAE: decreased from 3 ㏈ to –24 ㏈ SPL WRS: improved from 44% to 92%. Tinnitus and earfullness almost resolved. |
||||
| 38 days | PTA: improved from 33 ㏈ to 17 ㏈. DPOAE: increased from 7.1 ㏈ to 11.9 ㏈ SPL WRS: improved from 88% to 92%. |
||||
| Park SY (2022)12) | A-Tx, EA-Tx, PA-Tx, Hearing rehabilitation Chuna therapy | 0.30 ㎜×60 ㎜ 0.20 ㎜×30 ㎜ |
15 minutes | 20 weeks 2 times per week |
PTA(Left): improved from 35.83 ㏈ to 14.17 ㏈. PTA(Right): improved from 31.67 ㏈ to 10 ㏈ |
| Seo JI (2022)13) | A-Tx, H-med, Moxibustion | 0.25 ㎜×30 ㎜ | 10 minutes | 2months 1 time per week |
PTA: improved from 97.5 ㏈ to 27.5 ㏈. WRS: improved from ‘no response’ to 92%. SRT: improved from ‘no response’ to 20 ㏈ THI score: improved from 46 to 12 |
| Choi JW (2023)14) | A-Tx, H-med, Chuna therapy, Acupotomy | 0.20 ㎜×30 ㎜ | 20 minutes | 10 weeks 1 time per week |
PTA: improved from 34 ㏈ to 12 ㏈. SRT: improved from 40 ㏈ to 10 ㏈ ‡MML : improved from 49 ㏈ 29 ㏈ |
| Jung JW (2024)15) | A-Tx, Steam therapy, Moxibustion, EA-Tx | 0.20 ㎜×30 ㎜ | 15 minutes | 140 days | PTA: improved from 32.5 ㏈ to 20 ㏈. Tinnitus, earfullness resolved. |
| 97 days | PTA: improved from 37.5 ㏈ to 20 ㏈. Tinnitus, earfullness resolved. |
||||
| Kim SJ (2024)16) | A-Tx, Acupotomy, H-med | 0.25 ㎜×30 ㎜ | 15 minutes | 4 weeks 2 times per week |
PTA: improved from 49.5 ㏈ to 12.8 ㏈ tinnitus, earfullness, autophony resolved. Hearing ‡‡NRS decreased from 10 to 1 tinnitus NRS decreased from 10 to 1 |
| Zhong Y (2018)17) | A-Tx, Moxibustion | 0.30 ㎜×25 ㎜ | 20 minutes | 12 times | Complete recovery of hearing |
| He J (2018)18) | A-Tx, Moxibustion | ‡‡‡N.R | N.R | 9 weeks 2 times per week |
PTA: improved from 81 ㏈ to 50 ㏈. Tinnitus partially improved. |
| Kim MH (2018)19) | A-Tx EA-Tx, ¶TENS, Moxibustion | 0.25 ㎜×30 ㎜ | 10 minutes | admitted 3 weeks, 2 times per day, 1 month outpatient treatment | PTA: improved from 66.3 ㏈ to 51.3 ㏈, SRT: improved from 70 ㏈ to 30 ㏈, WRS: improved from 16% to 36%. |
| Arpornchayanon W (2019)20) | A-Tx, EA-Tx |
N.R | 20 minutes | 4 weeks, 3 times per week | PTA: 6000 ㎐ threshold improved from 55 ㏈ to 20 ㏈. Tinnitus resolved |
| 4 weeks, 3 times per week |
PTA: improved from 45 ㏈ to 18.75 ㏈, ‣PB score: improved from 88% to 100%. Tinnitus resolved |
||||
| Chen A (2019)21) | A-Tx | 0.25 ㎜×40 ㎜ | 30 minutes | 4 days 4 times | PTA: improved from 33 ㏈ to Normal range. |
| You C (2019)22) | A-Tx, Dexamethasone injection at acupoints | 0.25 ㎜×40 ㎜ | N.R | 9 days 5 times | PTA: improved from 42 ㏈ to Normal range. |
| LI J (2021)23) | A-Tx | 0.25 ㎜×40 ㎜ | 30 minutes | 28 times | Discomfort resolved |
| Liu Y (2023)24) | A-Tx, EA-Tx, Moxibustion, H-med | 0.25 ㎜×40 ㎜ | 30 minutes | 3 weeks 8 times | PTA: improved from 18.6 ㏈ to 6.4 ㏈. (125 ㎐ threshold improved from 35 ㏈ to 15 ㏈.) (250 ㎐ threshold improved from 30 ㏈ to 10 ㏈.) tinnitus resolved |
| Wang X (2023)25) | A-Tx, Exercise therapy (diaphragmatic breathing, Valsalva maneuver, tympanic membrane massage, occipital tapping) | 0.25 ㎜×40 ㎜ | 48 hours (manipulated once every 24 hours) | 5 days 5 times | PTA: improved from 55 ㏈ to 15 ㏈. Tinnitus resolved |
| Zhang J (2024)26) | A-Tx | needle | Less than 1 minute | 4 weeks, 2 times per week | PTA: improved from 90 ㏈ to 63 ㏈. THI score: improved from 46 to 12 |
| Zhao F (2024)27) | A-Tx, Moxibustion | 0.20 ㎜×25 ㎜, 0.30 ㎜×40 ㎜ | 20 minutes | 2 weeks 3 times per week | Markedly improved |
| Zhang Q (2024)28) | A-Tx, Moxibustion | 0.30 ㎜×50 ㎜, 0.25 ㎜×40 ㎜ | 30 minutes | 22 days 18 times | PTA: improved from 80 ㏈ to 50 ㏈. Tinnitus markedly decreased |
이 외 한약 치료 6편, 양약 치료 2편, 도침 치료 2편, 약침 치료 2편, 추나 치료 2편, 스테로이드제 경혈점 주사 1편, 증기 치료 1편, 건부항 치료 1편, 경피 신경 자극,(Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation, TENS) 1편, 운동 치료 1편, 소리 재활 치료 1편, 레이저 치료 1편에서 시행되었다.
침의 규격은 0.20 ㎜×30 ㎜, 0.25 ㎜×40 ㎜, 0.30 ㎜×60 ㎜등 다양하게 사용되었고, 두께는 0.25 ㎜가 9편으로, 가장 많이 사용되었다. 1편에서는 규격이 명시되지 않은 needle이 사용되었다.
유침 시간은 20분이 5편, 30분, 15분이 4편, 10분이 3편 1분 이내로 유침한 경우는 1편이었다. 1편에서는 유침을 하지 않았고, 1편에서는 유침 시간이 명시되지 않았다. 1편에서는 두정부에 침 치료를 시행한 후 48시간 유침을 하였고, 24시간마다 수기자극을 주었다.
가장 많이 사용된 혈위는 翳風(TE17)으로, 18편의 연구에서 사용되었고, 그 다음으로 聽宮(SI19) 16회, 耳門(TE21), 聽會(GB2) 12회, 百會(GV20) 11회, 風池(GB20) 9회, 合谷(LI4) 8회, 太衝(LR3) 6회, 足三里(ST36), 中渚(TE3) 5회, 完骨(GB12), 曲池(LI11), 俠谿(GB43), 外關(TE5) 3회 등이 사용되었다(Table 4).
평가지표로 순음청력검사를 활용한 23례 중 1례를 제외하고 평균 지표가 모두 호전되었고, Lee(각주)의 연구 3례 중 1례는 미국 이비인후과학회(American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery, AAO-HNS) guideline에 따라 호전되지 않은 것에 해당하나 250 ㎐의 Hearing level이 30 ㏈에서 15 ㏈로 감소하였고 이명, 자성강청, 이충만감 등 주관적 증상이 거의 소실되었다.
어음인지역치검사를 활용한 4례에서 모두 호전이 있었고, 그 중 2례는 무반응에서 각각 8 ㏈, 20 ㏈로 현저한 호전이 있었다. 단어인지도검사를 활용한 6례에서도 모두 호전이 있었고 그 중 1례에서는 무반응에서 92%로 현저한 호전이 있었다.
이명 장애 지수를 사용한 연구 3례 모두 30점 이상 감소하였고, 이명에 대한 주관적 호소를 평가지표로 활용한 16례 중 15례에서 호전이 있었고, 1례에서는 언급되지 않았다. 이 외 어지럼증, 자성강청, 두통, 이충만감 등을 호소하던 증례에서도 모두 증상이 호전되었다. 변조 이음향방사를 활용한 3례에서는 2례에서 호전이 있었고 1례에서는 3 ㏈에서 –24 ㏈로 악화되었다.
3례에서는 객관적 지표를 사용하지 않았으나, 그 중 1례에서는 난청 증상이 완전 회복되었다고 보고하였고 2례에서는 난청, 이명으로 인한 불편감이 완전히 소실되었다고 보고하였으며, 1례에서는 증상이 현저히 좋아졌다고 보고하였다(Table 3).
Ⅳ. 고 찰
돌발성 난청은 이과적 응급에 해당하는 질환으로서, 3일 내에 갑작스럽게 진행된 난청을 특징으로 하며, 대부분의 경우 원인을 찾지 못하나 혈관계의 장애, 바이러스 감염, 와우막 파열, 자가면역성 질환, 청신경 종양, 외림프누공 등이 원인으로 생각되고 있다. 가장 흔히 사용되는 청력 측정 기준은 순음청력검사에서 3개 이상의 연속된 주파수에서 30 ㏈ 이상의 감각신경성 난청이 3일 이내에 발생한 경우를 말하며, 일반적으로 일측성이나 드물게 양측성인 경우도 있고, 이명 어지럼증 등을 동반할 수 있다5).
회복의 예후는 환자의 나이, 발병 시 어지럼증의 유무, 청력 손실 정도, 청력 손실 시작과 치료 사이의 시간 등 여러 요인에 따라 달라질 수 있으나 발병 수일 내에 치료를 시작하면 비교적 예후가 양호하다. 일반적으로 환자의 32-65%가 자연적으로 회복될 수 있다고는 하나 청력이 회복되기 시작하는 2주 내에 치료를 시작하지 않으면 회복의 정도가 떨어질 수 있어 신 속하고 올바른 치료가 중요하다2). 스테로이드 치료에는 전신 스테로이드가 우선적으로 고려되고 때에 따라서 고실 내 스테로이드 주입술, 고압산소치료, 항바이러스제, 혈액순환개선제, 혈전용해제, 혈관 확장제 등이 고려될 수 있다5). 하지만 스테로이드의 경우 혈당 증가, 감염 취약성, 위장관출혈, 골다공증, 쿠싱 증후군 등의 부작용이 있고, 당뇨, 골다공증 심장병 등의 기저질환이 있는 환자에게는 투여에 주의가 필요하며, 특정 감염 질환 등 스테로이드 투여 금기인 경우도 있다29).
돌발성 난청은 暴聾, 卒聾에 범주에 해당하며, 邪渴少陽證, 肝鬱化火證, 氣血瘀阻證, 心脾兩虛證, 陰精虧虛證 등으로 변증할 수 있다. 변증에 따라 柴胡聰耳湯, 丹梔逍遙散, 補陽還五湯, 歸脾湯, 滋陰地黃湯 등을 활용할 수 있고, 翳風, 聽宮, 百會, 完骨, 聽會 등의 혈자리를 자침하여 치료한다1).
본 연구에 포함된 20편의 연구에는 침 치료를 중심으로, 여러 형태의 한의 치료의 분석이 이루어졌다. 치료에 활용된 혈위 분석 결과 가장 많이 사용된 혈위는 翳風(TE17)으로, 18편의 연구에서 사용되었고 聽 宮(SI19) 16편, 耳門(TE21), 聽會(GB2) 12편, 百會(GV20) 11편, 風池(GB20) 9편 合谷(LI4) 8편 등이 각각 사용되었다(table 4). 翳風(TE17)은 모든 耳病의 특효혈로서 귀를 지나는 手少陽三焦經과 足少陽膽經이 만나는 곳에 속하며 耳鳴聾을 치료한다. 또한 耳鳴, 耳聾의 약침 시술혈이다. 聽宮(SI19)은 聰耳작용이 있고, 益聽止痛, 寧神志 작용으로 귀 질환의 주요 혈위 중 하나이다. 耳門(TE21), 聽會(GB2)는 聽宮(SI19)과 마찬가지로 聰耳작용으로 제반 귀 질환에 활용된다. 百會(GV20)는 祛風淸熱 散邪解表작용으로 제반 五官 질병을 치료하며 耳鳴, 難聽등에 응용될 수 있다30,31).
치료에 활용된 혈위를 가장 많이 포함하고 있는 경락은 手少陽三焦經, 足少陽膽經, 手太陽小腸經, 督脈 순으로 나타났다. 手少陽三焦經, 足少陽膽經, 手太陽小腸經은 귀로 순행하여 경락 순행부 병증을 조절할 수 있으며, 督脈은 두정부를 지나는 경락으로서 제반 신경계 질환에 활용될 수 있다30,31)(Table 5).
병행치료로서 전침 치료를 활용한 6례를 분석한 결과 2 ㎐ 2례, 3 ㎐ 2례, 30 ㎐ 1례, 빈도수가 명시되지 않은 1례로 대체로 저빈도에서 중빈도의 빈도수를 활용해 치료하였다(Table 6). 강도는 3례에서 명시되었는데, Arponchayanon20)의 연구에서는 환자가 견딜 수 있는 최대강도로 전침 치료를 시행하였고, Kim19), Liu24)의 연구에서는 환자가 견딜 수 있는 강도라 명시하였다. 전침 자극 유지 시간은 10분 1례, 15분 2례, 20분 2례, 30분 1례로 다양하게 나타났다. 전침 치료 자극 혈자리는 翳風(TE17) (4회), 耳門(TE21), 聽宮(SI19), 完骨(GB12) (2회) 등이 활용되었다. 한 RCT 연구에서 돌발성 난청에 전침 치료를 활용할 때 2 ㎐, 50 ㎐, 2/50 ㎐ 혼합파 그룹 중 모든 전침군에서 유의미한 효과가 있었다고 하였고, 2/50 ㎐ 혼합파 그룹에서 치료율이 높았다고 보고하였다32). 저빈도 자극은 미세 순환을 개선하고 혈관 확장을 유도해 혈류 증가에 효과가 있고 감각신경 재활성화를 하여 신경 회복을 유도한다33). 고빈도 자극은 신경세포의 자발 발화를 억제하여 이명, 어지럼증 등 신경 과흥분 증상 완화를 기대할 수 있다34). 즉, 저빈도 전침을 기본으로, 환자 증상에 따라 고빈도 전침을 보조적으로 활용하는 것이 효과적임을 알 수 있다.
| First Author (Year) | Frequency | Intensity | Acupoints | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kim SY (2019)9) | 3 ㎐ | *N.R | 翳風(TE17) - 完骨(GB12) | 20 minutes |
| Park SY (2022)12) | Electroacupuncture with simultaneous electromagnetic stimulation | N.R | 15 minutes | |
| Jung JW (2024)15) | 3 ㎐ | N.R | 翳風(TE17) - 完骨(GB12) | 15 minutes |
| Kim MH (2024)19) | 30 ㎐ | adjusted to a tolerableble level | 耳門(TE21),聽宮(SI19), 聽會(GB2),下關(ST17), 翳風(TE17) | 10 minutes |
| Arpornchayanon W (2019)20) | 2 ㎐ | adjusted to the patient’s maximum tolerance | 聽宮(SI19) - 耳門(TE21) 瘈脈(TE18) - 翳風(TE17) 中渚(TE3) - 合谷(LI4) 太谿(KI3) - 太衝(LR3) | 20 minutes |
| Liu Y24) (2023) | 2 ㎐ | adjusted to a tolerable level | N.R | 30 minutes |
돌발성 난청 치료 가이드라인에 따르면, 증상 발생 후 최소 14일 이내에 스테로이드 요법을 쓸 것을 권장하며, 7일 이내에 스테로이드 요법을 시행해야 한다는 보고도 존재한다4). 본 연구에 포함된 김19)의 연구에서는 발병 93일 이후 스테로이드 요법을 시작했고, 42일간 치료하였으나 호전이 없었다. 한의 치료는 발병 8개월 후에 시작하였으나 21일간 입원 치료 및 한 달간 외래 치료 후 순음청력검사상 평균 역치가 66.3 ㏈에서 51.3 ㏈으로 호전되었고 어음청력검사상 지표가 다소 호전되었다. 김9)의 연구에서는 스테로이드 요법 없이 발병 3일 후 한의 치료를 시작해 8일간 입원치료 받은 후 순음청력검사 상 평균 역치가 75 ㏈에서 25 ㏈으로 감소하고, 이명은 90%이상 호전되었다고 언급하였다. 강10)의 연구에서는 스테로이드 요법 없이 발병 12일 후 한의 치료를 시작하였고, 60일간 치료 후 순음청력검사 상 평균 역치가 50 ㏈에서 12.5 ㏈으로 호전되었다. 이는 스테로이드 요법의 최적 투여 시기를 놓치거나 부득이하게 스테로이드 사용이 어려운 경우에, 한의 치료로도 유의미한 청력 회복을 기대해 볼 수 있음을 시사한다.
이명은 돌발성 난청의 흔한 동반 증상 중 하나로 난청 후 특정 주파수의 흥분 및 억제 신호의 불균형으로 인한 청각 중추의 자발 흥분의 증가로 인해 나타나거나 청력 소실 주파수를 표현하는 청각중추의 재구성화로 나타난다고 설명된다35).일시적 이명에 비해 돌발성 난청에 동반되는 이명의 정도가 더 강하고 난청의 치료 후에도 이명은 남아있는 경우가 있어 환자에게 큰 불편감을 야기할 수 있다36). 본 연구에 포함된 총 26례 중 25례에서 동반 증상으로 이명이 있었다. 이명의 치료경과를 언급한 논문 대부분이 이명에 큰 호전이 있었다고 하였으며, Zhang26), 강10), 서13)의 연구는 이명 장애 지수 설문(THI)을 활용하여 이명의 큰 호전이 있었음을 보고하였다. 앞선 내용은 돌발성 난청의 대표적인 동반 증상인 이명에도 효과가 있을 가능성을 제시한다.
돌발성 난청 환자의 이충만감은 중이 압력 이상에 기인하기보다는 청각과 체성감각간의 상호작용에 의해 발생할 수 있다37). 돌발성 난청 환자의 50%에서 많게는 83.7%에서 이충만감이 나타났다는 보고가 있었다37,38). 본 연구에 포함된 증례 중 10례에서만 이충만감을 호소하였는데, 이는 환자가 이충만감을 언급하지 않았거나 환자가 호소하였으나 연구에 포함되지 않았을 가능성이 있다고 사료된다. 이충만감은 돌발성 난청 환자의 삶의 질 측면에서 중요하므로 감9), 이11), 정15), 김16)의 연구에서 이충만감이 소실 혹은 호전되었다고 보고한 것은 주목할 만한 점이다.
어지럼증 또한 돌발성 난청에 동반될 수 있는데, 어지럼증이 동반될 경우 돌발성 난청의 예후가 불량하다는 보고가 있었다39). 본 연구에 포함된 연구 중 6례에서 어지럼증을 호소하였는데, 김9)의 연구에서 17일간 입원치료를 받은 후 어지럼증이 소실되었다고 보고하였다. 이 외 5례에서는 어지럼증에 대해 언급하지 않았다.
돌발성 난청의 역학에 관해 보고한 연구를 살펴보면, 남성과 여성의 발병률 차이는 크지 않고, 50대에서 60대에 유병률이 가장 높다고 한다2). 또한 드물게 소아, 청소년 환자에게서도 발생할 수 있다. 본 연구에 포함된 26례를 살펴보면 연령대별로 40대, 50대 6례, 60대 5례, 30대 4례 순으로 나타나 기존 연구와 유사한 연령 분포를 보였고, 소아, 청소년 환자에 해당하는 6세, 15세 대상 연구도 있었다.
Zhao27)의 연구에서는 6세 남자 환자가 2개월간 난청을 호소하고, 1주일 전 악화되어 1주일간 스테로이드 경구 투여받았으나 청력 호전이 없었다. 3주간 총 6번의 침구치료를 받은 이후 정상청력으로 회복되었다. Wang25)의 연구에서는 약물치료를 받지 않은 임산부에 발살바법, 복식호흡을 비롯한 운동요법, 침 치료를 활용해 치료하였다. 또한 두정부에 48시간 유침하며 24시간 마다 수기 자극을 주는 두침 치료를 시행하였다. 5일간 치료 후 순음청력검사상 평균 역치가 55 ㏈에서 15 ㏈로 호전되었고, 이명이 소실되었다. 위 증례들로 미루어보아 소아, 임산부 등 특수한 환자군에게도 다양한 방식의 침 치료를 적용할 수 있음을 알 수 있다.
이11)의 연구의 총 3례중 1례에서 순음청력검사상 평균 역치가 64 ㏈에서 18 ㏈, 어음명료도 검사상 44%에서 92%로 호전되었으나 DPOAE 검사상 -3 ㏈에서 -24 ㏈로 악화되었다. 이는 주관적 청각증상이나 순음청력검사상 호전으로 보아 와우내유모세포, 청신경 및 중추청각경로의 기능은 호전되었으나 와우외유모세포의 기능은 불완전하게 회복되었을 가능성이 있으며, 14일의 검사 간격으로 인한 측정 환경의 변화로 나타난 결과로도 해석될 수 있다.
3편의 연구가 이상반응이 없었음을 명시적으로 보고했고, 본 연구에 포함된 26례 모두에서 심각한 이상반응은 관찰되지 않았으나 대부분의 연구(17편)에서 이상반응 여부를 명시하지 않았다는 점에서 안정성에 대한 확정적인 결론을 내리기는 어렵다. 향후 연구에서는 이상반응 여부에 대한 보고가 필요하다고 사료된다.
본 연구에서는 총 26례의 돌발성 난청 증례를 대상으로 하여 침 치료의 임상 적용 양상과 치료 효과를 문헌 고찰의 방식으로 폭넓게 분석하였다. 순음청력검사, 어음청력검사 등 객관적 검사와 이명 장애 지수, 환자 주관적 증상 호소를 포함하여 치료 효과를 분석하고 침 치료 혈위, 전침 등 실제 임상 현장에서 활용되는 침 치료의 세부 사항을 구체화하였다는 점에서 의의가 있다.
다만 본 연구에 포함된 연구는 소규모 증례보고로 구성되어 있어 일반화 가능성이 낮고 침 치료가 돌발성 난청에 미치는 효과를 단정 짓기에는 무리가 있다는 점과 검색어의 한계로 모든 논문을 스크리닝 하지 못했다는 한계가 있다.
이에 향후 돌발성 난청의 한의 치료에 대한 추가적인 연구가 이루어져 돌발성 난청의 한방 치료의 안전성과 효과에 대한 근거 기반을 강화하고, 표준화된 치료 지침 확립에 기여할 수 있기를 기대하는 바이다.
Ⅴ. 결 론
Pubmed, OASIS, CNKI에서 돌발성 난청의 침 치료와 관련된 국내외 case study를 검색하여 분석한 결과 다음과 같은 결론을 얻었다.
-
돌발성 난청에 대한 침 치료의 유효성을 평가하기 위한 지표로 객관적 지표, 주관적 지표가 활용되었다. 객관적 지표는 순음청력검사, 어음인지역치검사, 단어인지도검사, 변조 이음향방사, 음소 균형 점수, 어음쾌적역치, 최소차폐역치 검사가 있었고, 주관적 지표는 이명장애지수, 환자 진술이 있었다.
-
침 치료에 많이 사용된 혈위는 翳風(TE17), 聽宮(SI19), 耳門(TE21), 聽會(GB2), 百會(GV20)였다.
-
침 치료와 함께 뜸 치료가 11편에서 사용되어 가장 많이 병행되었으며 그다음으로는 전침 치료, 한약치료가 6편에서 시행되었다. 그 외 양약 치료, 약침 치료, 추나치료, 증기치료, 부항치료, 운동치료, 소리재활치료, 경피신경자극, 스테로이드 경혈점 주사가 시행되었다.
-
돌발성 난청의 동반 증상으로 가장 많이 호소한 증상은 이명이며, 이충만감, 어지럼증, 자성강청 등이 있었다.
-
순음청력검사 결과를 평가 기준으로 사용한 23례에서 침 치료 후 유의미한 호전이 있었다.
-
총 20편의 논문 중 3편에서 이상반응이 없었다고 보고하였으며, 나머지 17편에서는 이상반응에 대해 명시하지 않았다.