Ⅰ. 서 론
돌발성 난청은 특별한 원인 없이 72시간 이내에 갑자기 발생하는 감각 신경성 난청이다. 순음청력검사 상 연속되는 3개 이상의 주파수에서 30㏈ 이상의 청력 저하가 있을 때 임상적으로 진단한다. 한국에서 유병률은 10만 명당 10명 이상으로 보고되며1), 건강보험심사평가원 통계상 돌발성 특발성 청력 소실(H91.2)로 진료를 받는 환자 수가 2009년에 50,119명에서 2018년에는 83,360명으로 증가하였다2).
돌발성 난청의 원인은 명확하지 않다. 다양한 원인이 병리 과정에 관여하며, 그 중 바이러스 감염과 혈관 순환 장애가 주된 발병기전으로 생각된다. 그 외 자가면역질환, 청신경 종양, 와우막 파열 등도 돌발성 난청의 원인 질환이 될 수 있다. 돌발성 난청의 자연 회복률은 부분적 청력 회복과 완전 회복을 포함하여 47-63% 정도이며, 임상적으로 전체 환자의 1/3은 정상 청력을 회복, 1/3은 40-60㏈가량의 청력을 소실, 나머지 1/3은 청력을 완전히 소실하는 것으로 보고된다. 대부분 발병 2주 이내에 호전되는 예후를 보이며 이 시기 안에 증상이 좋아지지 않으면 추후 회복률이 낮은 것으로 알려져 있으므로, 조기 진단과 치료가 매우 중요하다1).
돌발성 난청의 치료는 확실히 정립되어 있지 않아, 경험적 치료가 주로 시행되고 있다3).전신 스테로이드 요법이 가장 흔히 사용되는 치료이나, 속쓰림, 체중 증가, 불면증 및 혈당 증가 등의 부작용으로 인하여 최근에는 고실내 스테로이드 주입법이 자주 사용된다. 그 외에 항바이러스제, 항산화제, 항염증제, 혈액 순환개선제, 혈관확장제, 이뇨제 등이 사용되고 있으며, 고압산소요법이나 수술적 요법을 활용하기도 한다1).
현재까지 국내에 보고된 돌발성 난청의 한방치료에 대한 임상 논문은 국내에 발표된 치험례들을 분석한 이 등4)의 연구와 침 치료의 효과에 대해 분석한 김 등5)의 연구 등이 있으나 한약 치료에 대한 무작위 대조 임상시험(Randomized controlled trial, RCT) 연구를 종합하여 고찰한 논문은 없었다.
그러므로 본 연구에서는 중국에서 2017년 이후 보고된 논문 가운데 22편을 선정하여 돌발성 난청의 한약 치료에 대한 RCT 논문을 수집하였으며 치료 방법과 결과, 사용된 중재를 분석하여 한약 단독 치료 혹은 한약 치료와 양방 치료 병행의 유효성을 분석하고, 돌발성 난청의 한약 치료에 대한 임상적 근거로서 삼고자 한다.
Ⅱ. 연구 대상 및 방법
본 연구에서는 중국 데이터베이스인 China National Knowledge Infrastructure(CNKI)와 Wanfang med online을 이용하여 돌발성 난청의 한약 치료에 대한 RCT 논문을 검색하였다. 검색일은 2022년 1월 12일이었으며 최근 임상 연구 동향을 살펴보기 위해 검색 기간은 2017년 1월 1일부터 2021년 12월 31일까지 최근 5개년으로 한정하였다. 검색어는 ‘突发性耳聋 and 中药’, ‘突发性耳聋 and 中医’으로 하였다.
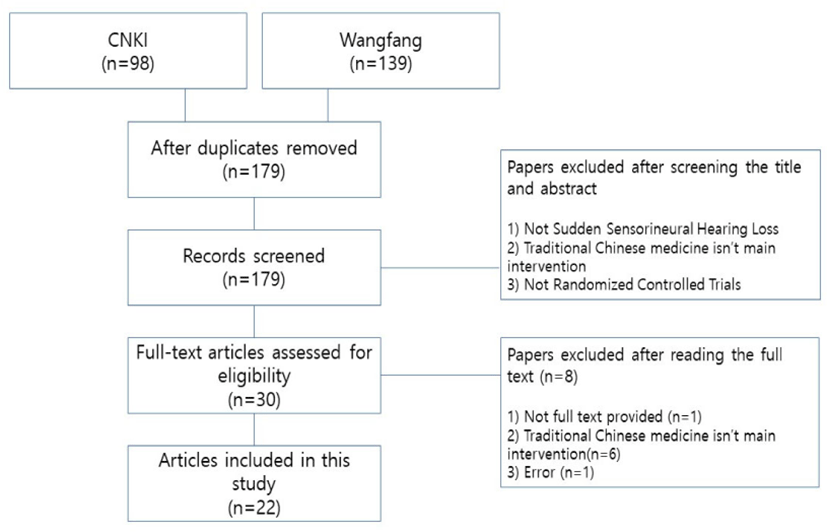
2개의 데이터베이스 검색을 통해 총 237편의 논문이 검색되었다. 이 중 중복된 논문을 우선 배제하였고, 남은 179편의 논문 중에서 제목과 초록을 바탕으로 RCT 논문 30편을 선정하였다. 중재는 한약 또는 한약과 양방 병용 치료이며 한약 외 다른 한방 치료를 사용한 경우는 제외하였다. 비교 중재는 양방 치료로 경구 약물과 주사제 등을 포함하였다. 이후 원문을 살펴 논문 전체가 제공되지 않는 것과 논문 자체의 오류가 있는 것을 제외하여 최종적으로 22편의 논문이 선정되었다(Fig. 1).
최종 선택된 논문들에서 연구 정보(저자, 발행연도), 대상자의 일반적인 특성(치료군과 대조군의 수와 나이, 질병 이환 기간)에 대한 정보를 표로 정리하였으며(Table 1), 각 평가 지표와 치료 방법, 치료 기간, 부작용에 관한 정보를 또 다른 표로 정리하였다(Table 2). 그리고 각 처방에 사용된 처방명과 한약재 구성을 표로 정리하였다(Table 3). 정리한 표를 바탕으로 사용된 한약재의 본초학적 분류, 사용된 빈도를 각각 따로 표로 정리하여 분석하였다(Table 4, 5).
| First Author (Year) | C* & T† Sample | Mean Age | Mean DI‡ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tang6) (2017) | C : 30 T : 30 | (38.70±12.65)y§ (41.93±10.23)y | (7.71±3.73)days (7.83±4.14)days |
| Wang7) (2017) | C : 35 T : 35 | (49.6±5.3)y (50.2±5.4)y | (7.6±2.3)days (7.4±2.2)days |
| Lian8) (2017) | C : 33 T : 33 | (49.09±15.78)y (48.25±16.13)y | (21.56±5.07)days (20.38±4.21)days |
| Zhao9) (2018) | C : 82 T : 81 | (47.5±3.7)y (47.6±3.5)y | (3.1±1.2)days (3.2±1.3)days |
| Yao10) (2018) | B : 50 A : 50 | (35.4±12.6)y (37.1±12.2)y | NR∥ NR |
| Tian11) (2018) | C : 30 T : 30 | (53.76±5.58)y (53.33±5.63)y | (8.57±1.34)days (8.39±1.28)days |
| Xue12) (2018) | C : 38 T : 38 | (40.15±4.31)y (40.23±4.17)y | (4.35±0.31)days (4.22±0.43)days |
| Ye13) (2019) | C : 30 T : 30 | (42.32±6.02)y (43.12±5.86)y | NR NR |
| Lai14) (2019) | C : 50 T : 50 | (38.59±7.66)y (37.84±9.32)y | NR NR |
| Jiang15) (2019) | C : 30 T : 30 | (55.57±3.28)y (56.24±3.14)y | NR NR |
| Wang16) (2019) | C : 70 T : 70 | (49.37±2.83)y (50.89±2.47)y | (4.96±1.41)days (5.32±1.63)days |
| Chen17) (2020) | C : 41 T : 41 | (36.24±12.35)y (37.15±13.02)y | (10.75±3.24)days (11.36±3.73)days |
| Qi18) (2020) | C : 34 T : 34 | (46.37±5.28)y (46.59±5.13)y | (14.52±3.19)days (14.29±3.57)days |
| Fu19) (2020) | C : 43 T : 44 | (35.46±2.71)y (36.05±2.24)y | (5.11±0.67)days (4.96±0.85)days |
| Sun20) (2020) | C : 37 T : 37 | (46.11±9.30)y (45.90±10.12)y | (16.12±2.02)days (15.91±1.93)days |
| Guo21) (2020) | C : 44 T : 44 | (64.2±1.7)y (63.6±1.3)y | (11.1±1.8)days (10.8±1.1)days |
| Lin22) (2020) | C : 30 T : 78 | (46.30±13.65)y (44.91±14.47)y | (5.28±3.19)days (5.43±2.93)days |
| Zhao23) (2020) | C : 60T : 60 | (44.87±11.51)y (44.53±11.62)y | (5.90±4.98)days (6±4.88)days |
| Dong24) (2021) | C : 30 T : 30 | (41.75±12.39)y (40.37±8.46)y | (4.56±2.22)days (4.25±1.98)days |
| Huang25 (2021) | C : 31 T : 31 | (42.07±1.23)y (42.52±1.22)y | (12.66±1.34)days (12.54±1.36)days |
| Pan26) (2021) | C : 36 T : 36 | (49.9±4.9)y (49.5±4.6)y | (4.72±0.71)days (4.91±0.82)days |
| Xia27) (2021) | C : 40 T : 40 | (45.05±13.58)y (46.21±14.36)y | (5.93±4.74)days (5.65±5.65)days |
| First Author (Year) | C* & T† Samples | Treatment Methods | Treatment Period | Scale | Efficacy Evaluation Criteria | Mean ㏈ before → after | Outcome & P value | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tang6) (2017) | C : 30 | - Vasodilator : Kaishi - Vitamin : B1, B12 |
14days | 1) Curative effect index(CEI) 2) Symptom score(deafness, tinnitus, dizzness) 3) Hemorheology(Blood coagulation time) |
CEI -Healing: 95%≤symptom score reduction -Significant effective: 70%≤symptom score reduction<95%; -Effective: 30%≤symptom score<70% -Ineffective: symptom product reduction<30% *Symptom : deafness, tinnitus, dizzness |
(43.84±12.11)㏈ → NR∥ |
CEI C : 66.7% T : 86.7% (p<0.05) |
NR |
| T : 30 | - HM‡(OA§) bid with C | (40.39±10.57)㏈ → NR |
||||||
| Wang7) (2017) | C : 35 | - Vasodilator : Alprostadil - Vitamin : Mecobalamin, Niacin |
14days | 1) TER¶ 2) PTA** 2) Total symptom scores(tinnitus, dizziness, ear fullness) |
TER -Healing: normal hearing -Significantly effective: PTA is increased by more than 30㏈ -Effective: PTA is increased by 15-30㏈ -Ineffective: PTA is increased by less than 15㏈ |
(70.5±19.6)㏈ → (62.2±21.2)㏈ |
TER C : 71.4% T : 91.7% (p<0.05) |
NR |
| T : 35 | - HM(OA) bid | (71.2±20.3)㏈ → (50.6±19.4)㏈ |
||||||
| Lian8) (2017) | C : 33 | - Blood Circulating Agent : Ginkgo biloba capsule - Vitamin : Methylcobalamin |
14days | 1) TER 2) PTA 3) Total symptom percent(tinnitus, dizziness, ear fullness) |
TER -Healing: PTA returns to normal, or reaches the level of healty ear, or reaches the level before the illness. -Significant effecttive: PTA is improved by more than 30㏈. -Effective: PTA is improved by 15-29㏈ -Ineffective: PTA is improved by less than 14㏈ |
(56.4±14.57)㏈ → (35.75±20.61)㏈ |
TER C : 33.33% T : 84.85% (p<0.05) |
NR |
| T : 33 | - HM(OA) bid | (58.26±16.21)㏈ → (49.32±22.73)㏈ |
||||||
| Zhao9) (2018) | C : 82 | - Vitamin : Methylcobalamin - Corticosteroid : Dexamethasone - Vasoactive drug : Buflomedil |
15days | 1) TER 2) PTA |
NR | (63.29±17.37)㏈ → (40.24±15.61)㏈ |
TER C : 82.72% T : 98.78% (p<0.05) |
NR |
| T : 81 | - HM(OA) qd with C | (63.24±17.36)㏈ → (31.47±14.55)㏈ |
||||||
| Yao10) (2018) | B : 50 | - Corticosteroid : Dexamethasone - Anti-vertigo medication : Betahistine - Vitamin : mecobalamin, B1 |
14days | 1) TER | TER -Healing: normal PTA at 250-4,000㎐, hearing is restored to before the illness, and symptoms disappear. -Effective: PTA at 50-4000㎐ is improved by more than 15㏈, and symptoms are improved. -Ineffective: Symptoms are not relieved or even worsened. *Symptom : tinnitus, dizziness |
NR | TER B : 78.0% A : 96.0% (p<0.05) |
B : 18.0% A : 4.0% (p<0.05) |
| A : 50 | - HM(OA) bid with B | NR | ||||||
| Tian11) (2018) | C : 30 | - Anti-vertigo medication : Betahistine - Blood Circulating Agent : Shuxuening |
28days | 1) TER 2) Disease socres(deafness, tinnitus, dizziness) |
TER -Healing: Symptoms return to normal, and disease scores are reduced by 90% or more than before treatment. -Significantly effective: Symptoms return to normal , and disease scores are reduced by 70-89%. -Effective: Symptoms have improved, and symptom score is reduced by 30-69%. -Ineffective: Does not meet the above requirements. *Symptoms : deafness, tinnitus, dizziness |
NR | TER C : 76.67% T : 96.67% (p<0.05) |
Not serious side effect |
| T : 30 | - HM(OA) bid with C | NR | ||||||
| Xue12) (2018) | C : 38 | - Corticosteroid : Dexamethasone - Coenzyme : Coenzyme A | 14days | 1) TER 2) Hemorheology(Whole blood viscosity) |
TER -Healing: Symptoms disappear completely, and PTA is completely restored. -Significantly effective: Symptoms have basically disappeared, and PTA is improved by more than 30㏈. -Effective: Symptoms have improved, and P is improved by 15-30㏈. -Ineffective: No relief of clinical symptoms, even serious. *Symptoms : tinnitus, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, nystagmus |
NR | TER C : 78.95% T : 97.37% (p<0.05) |
Not serious side effect |
| T : 38 | - HM(OA) bid with C | NR | ||||||
| Ye13) (2019) | C : 30 | - Blood Circulating Agent : Ginkgo biloba extract tablets, Citicoline sodium tablets - Anti-vertigo medication : Betahistine, Flunarizine capsules - Corticosteroid : Dexamethasone(Injection intratympanic) |
14days | 1) TER 2) PTA 3) Symptoms(tinnitus, dizziness, ear fullness) |
TER -Healing: Symptoms disappeared, PTA returned to normal. -Significant effective: Symptoms basically disappeared, PTA is improved by more than 30㏈. -Effective: Symptoms improved, PTA is increased by 15-30㏈ -Ineffective: No significant change *Symptoms : tinnitus, dizziness, ear fullness |
(67.03±15.61)㏈ → (49.23±21.61)㏈ |
TER C : 63.33% T : 76.67% (p>0.05) |
NR |
| T : 30 | - HM(OA) bid with C | (67.80±15.02)㏈ → (46.17±21.47)㏈ |
||||||
| Lai14) (2019) | C : 50 | - Vasodilators - Hormonal drugs |
14days | 1) TER | TER -Healing: normal hearing, normal PTA, tinnitus and dizziness disappear. -Effective: PTA is improved by more than 30㏈, tinnitus and dizziness are alleviated, and sleep is not affected. -Ineffective: PTA is increased by less than 15㏈, tinnitus and dizziness are not improved, which affects sleep |
NR | TER C : 84.0% T : 96.0% (p<0.05) |
Not serious side effect |
| T : 50 | - HM(OA) bid with C | NR | ||||||
| Jiang15) (2019) | C : 30 | - Vasodilators : Vinpocetine | 10days | 1) TER 2) PTA 3) Dizziness |
TER -Healing: PTA at 0.25-4k㎐ returns to the normal level or reaches the level before the illness. -Significant effective: PTA at 0.25-4k㎐ is improved by more than 30㏈. -Effective: PTA at 0.25-4k㎐ is improved by 15-30㏈. -Invalid: PTA at 0.25-4k㎐ is improved by less than 15㏈. |
(62.46±9.64)㏈ → (52.16±8.02)㏈ |
TER C : 50.0% T : 66.7% (p<0.05) |
NR |
| T : 30 | - HM(OA) bid with C | (63.25±8.86)㏈ → (45.71±8.17)㏈ |
||||||
| Wang16) (2019) | C : 70 | - Corticosteroid : Methylprednisolone (Injection. skin behind the ears) |
14days | 1) TER 2) PTA 3) Hemorheology(plasma viscosity, blood coagulation time, hematocrit, Homocysteine) |
TER -Healing: noraml PTA or reaches the level of the healthy ear -Significantly effect: PTA is improved by more than 30㏈. -Effective: PTA is improved by 15-30㏈. -Ineffective: PTA is improved by less than 15㏈. |
(73.48±9.70)㏈ → (41.37±7.65)㏈ |
TER C : 78.57% T : 85.71% (p<0.05) |
C : 11.43% T : 4.29% (p>0.05) |
| T : 70 | - HM(OA) bid with C | (74.53±8.96)㏈ → (33.61±6.42)㏈ |
||||||
| Chen17) (2020) | C : 41 | - Corticosteroid : Prednisone acetate tablets - Vasodilator : Alprostadil |
10days | 1) TER 2) PTA 3) Deafness 4) Total symptoms scores(deafness, tinnitus, ear fullness, dark red lips) |
TER -Healing: Symptoms disappeared, impaired PTA returned to normal. -Significant effective: Symptoms basically disappeared, PTA is improved by more than 30㏈. -Effective: Symptoms improved, PTA is increased by 15-30㏈ -Ineffective: No significant change *Symptoms : deafness, tinnitus, ear fullness, dark red lips |
(65.12±8.31)㏈ → (48.28±7.62)㏈ |
TER C : 73.2% T : 90.2% (p<0.05) |
NR |
| T : 41 | - HM(OA) bid with C | (67.32±8.23)㏈ → (41.61±5.37)㏈ |
||||||
| Qi18) (2020) | C : 34 | - Vitamin : Mecobalamin vitamin C - Vasodilator : Alprostadil - Corticosteroid : Dexamethasone |
14days | 1) TER 2) PTA 3) Hemorheology(plasma viscosity, fibrinogen, hematocrit) |
TER -Healing: normal PTA, or returns to the level of the uninfected side, or the level before the illness. -Significant effective: PTA is improved by more than 30㏈. -Effective: PTA is improved by 15-30㏈. -Ineffective: PTA is improved by less than 15㏈. |
(63.25±10.48)㏈ → (40.53±8.14)㏈ |
TER C : 70.59% T : 91.18% (p<0.05) |
C : 17.65% T : 14.71% (p>0.05) |
| T : 34 | - HM(OA) bid with C | (63.14±10.29)㏈ → (48.75±9.26)㏈ |
||||||
| Fu19) (2020) | C : 43 | - Vasodilator : Alprostadil - Nerve growth factor |
14days | 1) TER 2) Hemorheology(whole blood viscosity, plasma viscosity, fibrinogen, hematocrit) 3) Total symptoms scores(deafness, tinnitus, dizziness, dark red tongue, petechia) |
TER -Healing: PTA returns to normal or healthy ears or before the onset, the syndrome score reduction is greater than 90%. -Significant effective: PTA is increased by more than 30㏈, and the syndrome score is reduced by 60% to 89%. -Effective: PTA is increased by 15-29㏈, and the syndrome score decreases by 30% to 59%. -Ineffective: PTA did’t increase significantly, and the syndrome score decreased by less than 29%. *Symptoms : deafness, tinnitus, dizziness, dark red tongue, petechia |
NR | TER C : 72.09% T : 93.18% (p<0.05) |
NR |
| T : 44 | - HM(OA) bid with C | NR | ||||||
| Sun20) (2020) | C : 37 | - Corticosteroid : Prednisone - Vasodilator : Alprostadil - Vitamin : Mecobalamin |
14days | 1) TER 2) PTA 3) Plasma lipids 4) Atherogenic index of plasma |
TER -Healing: normal hearing -Significantly effective: PTA is increased by more than 30㏈. -Effective: PTA is increased by 15-30㏈. -Ineffective: PTA is increased by less than 15㏈ |
(62.43±11.88)㏈ → (49.08±14.71)㏈ |
TER C : 67.50% T : 78.05% (p<0.05) |
NR |
| T : 37 | - HM(OA) bid with C | (63.37±10.82)㏈ → (40.54±13.70)㏈ |
||||||
| Guo21) (2020) | C : 44 | - Vasodilator : Alprostadil - Vitamin : Mecobalamin, Niacin |
14days | 1) TER 2) PTA 3) Symptom score(deafness, tinnitus, dizzness) |
TER -Healing: Symptoms disappear, and PTA returns to normal -Effective: Symptoms are improved, PTA is increased by more than 15㏈ -Ineffective: Inconsistent with the above description. |
(72.94±14.77)㏈ → (62.02±15.92)㏈ |
TER C : 75.00% T : 95.45% (p<0.05) |
NR |
| T : 44 | - HM(OA) bid | (73.22±12.08)㏈ → (50.25±16.24)㏈ |
||||||
| Lin22) (2020) | C : 30 | - Vitamin : Methylcobalamin - Blood Circulating Agent : Ginkgo biloba extract - Corticosteroid : Methylprednisolone |
10-14days | 1) TER 2) PTA 3) Symptom score( tinnitus, dizzness, ear fullness) |
TER -Healing: PTA returns to normal, or reaches the level of healty ear, or reaches the level before the illness. -Significantly effective: PTA is improved by more than 30㏈. -Effective: PTA is improved by 15-30㏈. -Ineffective: PTA is improved by less than 15㏈. |
(55.23±15.61)㏈ → (38.47±18.35)㏈ |
TER C : 60.0% T : 79.49% (p<0.05) |
NR |
| T : 78 | - HM(OA) with C | (54.64±12.73)㏈ → (33.18±13.55)㏈ |
||||||
| Zhao23) (2020) | C : 60 | - Corticosteroid : Dexamethasone - Blood Circulating Agent : Troxerutin cerebroprotein hydrolysate - Nerve growth factor |
14days | 1) TER 2) Tinnitus |
TER -Healing: normal hearing or reaches the level before the illness -Significantly effective: PTA is improved by more than 30㏈. -Effective: PTA is improved by 15-30㏈. -Ineffective: PTA is improved by less than 15㏈. |
NR | TER C : 66.66% T : 90.0% (p<0.05) |
C : 6.67% T : 13.34% (p>0.05) |
| T : 60 | - HM(OA) bid with C | NR | ||||||
| Dong24) (2021) | C : 30 | - Corticosteroid : Dexamethasone(injecion IV & intratympanic) - Blood Circulating Agent : Troxerutin cerebroprotein hydrolysate, Shuxuening - Nerve growth factor |
14days | 1) TER 2) Symptom score (dizziness, tinnitus, deafness) |
TER -Healing: PTA at 0.5-4k㎐ reaches normal, or to the hearing value of healthy ears, or to the hearing value before illness -Significant effective: PTA at 0.5-4k㎐ is improved by more than 30㏈ -Effective: PTA is improved by 15-30㏈ -Ineffective: PTA is improved by less than 15㏈. |
NR | TER C : 63.33% T : 86.67% (p<0.05) |
NR |
| T : 30 | - HM(OA) bid with C | NR | ||||||
| Huang25) (2021) | C : 31 | - Corticosteroid : Prednisone - Viatamin : Mecobalamin - Blood Circulating Agent : Ginkgo biloba extract |
14days | 1) TER 2) PTA 3) Hemorheology(Fibrinogen, Plasma viscosity, whole blood viscosity) 4) Symptoms score(ear fullness, tinnitus, dizziness, nausea<vomiting) |
TER -Significantly effective: symptoms disappeared or syndrome scores are reduced by more than 70%, and normal hearing. -Effective: symptoms are significantly improved, syndrome scores are reduced by more than 50%, PTA is improved by more than 15㏈ -Ineffective: PTA is improved less than 15㏈, symptoms are not improved or even worse. *Symptom : ear fullness, tinnitus, dizziness, nausea, vomiting |
(64.33±8.65)㏈ → (44.37±5.77)㏈ |
TER C : 74.19% T : 96.77% (p<0.05) |
C : 12.90% T : 6.45% (p>0.05) |
| T : 31 | - HM(OA) hs with C | (64.27±8.76)㏈ → (39.74±5.82)㏈ |
||||||
| Pan26) (2021) | C : 36 | - Vasodilators - Nerve nutrition - Anticoagulation - Corticosteroid |
14days | 1) TER 2) PTA |
TER -Healing: normal hearing, symptoms disappear -Significant effective: PTA is increased by more than 30㏈, symptoms are significantly reduced. -Effective: PTA is increased by 15-30㏈, symptoms are reduced. -Ineffective: Does not meet the above criteria |
(63.78±9.61)㏈ → (42.23±6.65)㏈ |
TER C : 76.7% T : 95.1% (p<0.05) |
TER C : 16.77% T : 11.1% (p>0.05) |
| T : 36 | - HM(OA) bid with C | (62.05±8.63)㏈ → (31.17±4.13)㏈ |
||||||
| Xia27) (2021) | C : 40 | - Corticosteroid : Dexamethasone | NR | 1) TER 2) Symptom(tinnitus, deafness, ear fullness) |
TER -Healing: PTA returns to the normal level, or reaches the level of healthy ear, or reaches the level before the illness. -Significantly effective: PTA is improved by more than 30㏈. -Effective: PTA is improved by 15-30㏈. -Ineffective: PTA is improved by less than 15㏈. |
NR | PTA C : 72.5% T : 87.5% (p<0.05) |
NR |
| T : 40 | - HM(OA) with C | NR |
| First Author (Year) | Name of Herb Medicine | Pattern Differentiation | Herb Medicine of Decoction(each herb) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tang6) (2017) | Ertong No.2-fang (耳聾2號方) | Qi stagnation and blood stasis type (氣滯血瘀型) | Cnidii Rhizoma(川芎), Angelicae Gigantis Radix(當歸), Salviae Militiorrhizae Radix(丹參), Persicae Semen(桃仁), Acori Graminei Rhizoma(石菖蒲), Bupleuri Radix(柴胡), Curcumae Radix(鬱金), Cyperi Rhizoma(香附子), Paeoniae Radix Alba(白芍藥), Lumburicus(地龍), Puerariae Radix(葛根), Liquidambaris Fructus(路路通), Os Draconis(龍骨), Ostreae Testa(牡蠣), Magnetitum(磁石), Ramulus et Uncus(釣鉤藤) |
| Wang7) (2017) | Tongqiao Huoxue –tang combined with Tongqi-san (通竅活血湯配合通氣散) | Qi stagnation and blood stasis type (氣滯血瘀型) | Achyranthis Radix(牛膝), Curcumae Radix(鬱金), Puerariae Radix(葛根), Boiled Astragali Radix(炙黃芪), Angelicae Gigantis Radix(當歸), Rehmanniae Radix Preparata(生地黃), Paeoniae Radix Rubra(赤芍藥), Acori Graminei Rhizoma(石菖蒲), Persicae Semen(桃仁), Carthami Flos(紅花), Aurantii Fructus Immaturus(枳殼), Bupleuri Radix(柴胡), Platycodonis Radix(桔梗), Citri Unshius Pericarpium(陳皮), Cyperi Rhizoma(香附子), Cicadae Periostracum(蟬蛻), Glycyrrhizae Radix(甘草) |
| Lian8) (2017) | NR | Hyperactivity of liver yang (肝陽上亢) | Nardotidis seu Sulculii Concha(石決明), Gypsum(石膏), Magnetitum(磁石), Tribuli Fructus(白蒺藜), Puerariae Radix(葛根), Lumburicus(地龍), Scutellariae Radix(黃芩), Paeoniae Radix Rubra(赤芍藥), Paeoniae Radix Alba(白芍藥), Acori Graminei Rhizoma(石菖蒲), Fired Oryzae Fructus Germinatus(炒穀芽), Chrysanthemi Morifolii Flos(菊花), Powder of Antelopis Cornu(羚羊角粉), Penthorum chinense(趕黃草), Polygonati Rhizoma(黃精), Ligustri Fructus(女貞子) |
| Zhao9) (2018) | NR | NR | Scutellariae Radix(黃芩), Carthami Flos(紅花), Paeoniae Radix Rubra(赤芍藥), Salviae Militiorrhizae Radix(丹參), Angelicae Gigantis Radix(當歸), Bupleuri Radix(柴胡), Acori Graminei Rhizoma(石菖蒲), Bambusa textilis McClure(青皮), Cnidii Rhizoma(川芎) |
| Yao10) (2018) | NR | NR | Persicae Semen(桃仁), Carthami Flos(紅花), Rehmanniae Radix Preparata(生地黃), Aurantii Fructus Immaturus(枳殼), Angelicae Gigantis Radix(當歸), Paeoniae Radix Rubra(赤芍藥), Puerariae Radix(葛根), Salviae Militiorrhizae Radix(丹參), Bupleuri Radix(柴胡), Cnidii Rhizoma(川芎) |
| Tian11) (2018) | Qinggan Tongqiao-tang (清肝通竅湯) | liver-fire disturbance (肝火上擾) | Salviae Militiorrhizae Radix(丹參), Puerariae Radix(葛根), Angelicae Gigantis Radix(當歸), Alismatis Rhizoma(澤瀉), Scutellariae Radix(黃芩), Rehmanniae Radix Preparata(生地黃), Cnidii Rhizoma(川芎), Bupleuri Radix(柴胡), Acori Graminei Rhizoma(石菖蒲), Gentianae Scabrae Radix(龍膽草), Polygalae Radix(遠志), Gardeniae Fructus(梔子) |
| Xue12) (2018) | Conger Tongqiao-tang (聰耳通竅湯) | NR | Achyranthis Radix(牛膝), Angelicae Gigantis Radix(當歸), Rehmanniae Radix Preparata(生地黃), Paeoniae Radix Rubra(赤芍藥), Acori Graminei Rhizoma(石菖蒲), Persicae Semen(桃仁), Carthami Flos(紅花), Aurantii Fructus Immaturus(枳殼), Bupleuri Radix(柴胡), Platycodonis Radix(桔梗), Cnidii Rhizoma(川芎), Cyperi Rhizoma(香附子), Glycyrrhizae Radix(甘草) |
| Ye13) (2019) | Yier Tongqiao -tang (益耳通竅湯) | NR | Persicae Semen(桃仁), Carthami Flos(紅花), Paeoniae Radix Rubra(赤芍藥), Cnidii Rhizoma(川芎), Moutan Cortex Radicis(牧丹皮), Puerariae Radix(葛根), Rehmanniae Radix Preparata(熟地黃), Liquidambaris Fructus(路路通), Acori Graminei Rhizoma(石菖蒲), Calcined Magnetitum(煅磁石), Boiled Drynariae Rhizoma(烫骨碎補) |
| Lai14) (2019) | Longdan Xiegan-tang (龍膽瀉肝湯) | Disturbed by liver and gallbladder heat (肝膽實火上擾) | Scutellariae Radix(黃芩), Gardeniae Fructus(梔子), Akebiae Caulis(木通), Plantaginis Semne(車前子), Gentianae Scabrae Radix(龍膽草), Glycyrrhizae Radix(甘草), Alismatis Rhizoma(澤瀉), Angelicae Gigantis Radix(當歸), Rehmanniae Radix Preparata(生地黃), Bupleuri Radix(柴胡) |
| Yin Qiao-san (銀翹散) | Offenders of wind (風邪外犯) | Forsythiae Fructus(連翹), Lonicerae Flos(金銀花), Arctii Fructus(牛蒡子), Platycodonis Radix(桔梗), Menthae Herba(薄荷), Glycyrrhizae Radix(甘草), Schizonepetae Spica(芥穗), Glycine Semen Preparata(淡豆豉), Phyllostachyos Folium(竹葉) | |
| Tongqiao Huoxue -tang (通竅活血湯) | Blood stasis blocking collaterals (瘀血阻絡) | Paeoniae Radix Rubra(赤芍藥), Cnidii Rhizoma(川芎), Persicae Semen(桃仁), Carthami Flos(紅花), Moschus(麝香), Zizyphi Fructus(去核紅棗), Allii Fistulosi Bulbus(老蔥), Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens(鮮薑) | |
| Jiang15) (2019) | Sijunzi-tang (四君子湯) | Weak spleen type (脾氣虛弱) | Codonopsis Pilosulae Radix(黨參), Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba(白朮), Poria Sclerotium(茯苓), Boiled Glycyrrhizae Radix(炙甘草), Alismatis Rhizoma(澤瀉), Os Draconis(龍骨), Gastrodiae Rhizoma(天麻) |
| Banha Baekchul Cheonma-tang (半夏白朮天麻湯) | Phlegm turbidity moderate resistance type (痰濁中阻) | Pinelliae Rhizoma(法半夏), Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba(白朮), Gastrodiae Rhizoma(天麻), Poria Sclerotium(茯苓), Boiled Glycyrrhizae Radix(炙甘草), Tomentose Pummelo(化橘紅), Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens(生薑), Salviae Militiorrhizae Radix(丹參) | |
| Qiju Dihuang-tang (杞菊地黃湯) | Kidney essence deficiency type (腎精虧虛) | Fructus Lycii(枸杞子), Chrysanthemi Flos(菊花), Rehmanniae Radix Preparata(熟地黃), Dioscoreae Rhizoma(山藥), Cornus officinalis(山茱萸), Moutan Radicis Cortex(牡丹皮), Poria Sclerotium(茯苓), Alismatis Rhizoma(澤瀉), Gastrodiae Rhizoma(天麻), Uncariae Ramulus cum Uncus(釣鉤藤) | |
| Wang16) (2019) | Buzhong Yiqi-tang (補中益氣湯) | NR | Astragali Radix(黃芪), Boiled Glycyrrhizae Radix(炙甘草), Codonopsis Pilosulae Radix(黨參), Angelicae Gigantis Radix(當歸), Citri Unshius Pericarpium(陳皮), Cimicifuga rhizome(升麻), Bupleuri Radix(柴胡), Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba(白朮) |
| Chen17) (2020) | NR | NR | Acori Graminei Rhizoma(石菖蒲), Salviae Militiorrhizae Radix(丹參), Persicae Semen(桃仁), Carthami Flos(紅花), Angelicae Gigantis Radix(當歸), Paeoniae Radix Rubra(赤芍藥),Cnidii Rhizoma(川芎), Liquidambaris Fructus(路路通), Bupleuri Radix(柴胡), Ligustri Fructus(女貞子), Fructus Lycii(枸杞子), Glycyrrhizae Radix(甘草) |
| Qi18) (2020) | NR | Qi stagnation and blood stasis type (氣滯血瘀型) | Boiled Astragali Radix(炙黃芪), Paeoniae Radix Rubra(赤芍藥), Curcumae Radix(鬱金), Puerariae Radix(葛根), Polygonati Rhizoma(黃精), Cnidii Rhizoma(川芎), Acori Graminei Rhizoma(石菖蒲), Carthami Flos(紅花), Persicae Semen(桃仁), Armeniacae Semen(杏仁), Citri Unshius Pericarpium(陳皮), Platycodonis Radix(桔梗), Cicadae Periostracum(蟬蛻), Glycyrrhizae Radix(甘草) |
| Fu19) (2020) | Tongluo Kaiqiao- fang (通絡開竅方) | NR | Salviae Militiorrhizae Radix(丹參),Persicae Semen(桃仁), Cnidii Rhizoma(川芎), Angelicae Dhuricae Radix(白芷), Asari Radix et Rhizoma(細辛), Acori Graminei Rhizoma(石菖蒲), Pinelliae Rhizoma(半夏), Bupleuri Radix(柴胡), Angelicae Gigantis Radix(當歸), Glycyrrhizae Radix(甘草) |
| Sun20) (2020) | Tongqiao Huoxue-tang (通竅活血湯) | Qi stagnation and blood stasis type (氣滯血瘀型) | Achyranthes bidentata Blume(牛膝), Salviae Militiorrhizae Radix(丹參), Carthami Flos(紅花), Cnidii Rhizoma(川芎), Angelicae Gigantis Radix(當歸), Paeoniae Radix Rubra(赤芍藥), Persicae Semen(桃仁), Angelicae Dhuricae Radix(白芷), Acori Graminei Rhizoma(石菖蒲), Bupleuri Radix(柴胡), Cicadae Periostracum(蟬蛻), Aurantii Fructus Immaturus(枳殼), Platycodonis Radix(桔梗), Glycyrrhizae Radix(甘草), Allii Fistulosi Bulbus(蔥白), Zizyphi Fructus(大棗) |
| Guo21) (2020) | Tongqiao Huoxue-tang combined with Tongqi-san (通竅活血湯配合通氣散) | Qi stagnation and blood stasis type (氣滯血瘀型) | Rehmanniae Radix Preparata(熟地黃), Puerariae Radix(葛根), Achyranthes bidentata Blume(牛膝), Acori Graminei Rhizoma(石菖蒲), Boiled Astragali Radix(炙黃芪), Paeoniae Radix Rubra(赤芍藥), Curcumae Longae Rhizoma(薑黃), Angelicae Gigantis Radix(當歸), Platycodonis Radix(桔梗), Persicae Semen(桃仁), Carthami Flos(紅花), Cyperi Rhizoma(香附子), Aurantii Fructus Immaturus(枳殼), Citri Unshius Pericarpium(陳皮), Bupleuri Radix(柴胡), Glycyrrhizae Radix(甘草) |
| Lin22) (2020) | Guipi-tang (歸脾湯) | Qi and blood deficiency (氣血虧虛) | Codonopsis Pilosulae Radix(黨蔘), Astragali Radix(黃芪), Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba(白朮), Angelicae Gigantis Radix(當歸), Longan Arillus(龍眼肉), Zizyphi Semen(酸棗仁), Poria Sclerotium Cum Pini Radix(茯神), Polygalae Radix(遠志), Zizyphi Fructus(大棗), Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens(生薑), Aucklandiae Radix(木香), Boiled Glycyrrhizae Radix(炙甘草) |
| Zhao23) (2020) | NR | NR | Euonymi Ramuli Suberalatum(鬼箭羽), Schisandrae Fructus(五味子), Acori Graminei Rhizoma(石菖蒲), Puerariae Radix(葛根), Polygalae Radix(遠志), Alismatis Rhizoma(澤瀉), Mori Fructus(桑椹子), Curcumae Radix(鬱金), Magnetitum(磁石), Viticis Fructus(蔓荊子), Cicadae Periostracum(蟬蛻), Rehmanniae Radix Preparata(熟地黃), Cornus officinalis(山茱萸), Calcined Ostreae Testa(煅牡蠣) |
| Dong24) (2021) | Qianyang Fengsui -dan (潛陽封髓丹) | NR | Aconiti Lateralis Radix Preparata(附子), Amomi Fructus(砂仁), Testudinis Carapax et Plastrum(龜板), Phellodendri Cortex(黃柏), Glycyrrhizae Radix(甘草) |
| Huang25) (2021) | Tongqiao Huoxue-tang (通竅活血湯) | Qi stagnation and blood stasis type (氣滯血瘀型) | Paeoniae Radix Rubra(赤芍藥), Cnidii Rhizoma(川芎), Carthami Flos(紅花), Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens(鲜生薑), Persicae Semen(桃仁研泥), Removed seed, Zizyphi Fructus(大棗去核), Allii Fistulosi Bulbus(老葱), Moschus(麝香绢包) |
| Pan26) (2021) | Huoxue Liqi Tongqi-tang (活血理氣通氣湯) | Qi stagnation and blood stasis type (氣滯血瘀型) | Salviae Militiorrhizae Radix(丹參), Persicae Semen(桃仁), Carthami Flos(紅花), Bupleuri Radix(柴胡), Cyperi Rhizoma(香附子), Curcumae Radix(鬱金), Cnidii Rhizoma(川芎), Acori Graminei Rhizoma(石菖蒲), Polygalae Radix(遠志), Puerariae Radix(葛根), Glycyrrhizae Radix(甘草) |
| Xia27) (2021) | Wendan-tang (溫膽湯) | Phlegm and Fire Stagnation (痰火鬱結) | Pinelliae Rhizoma(姜半夏), Poria Sclerotium(茯苓), Citri Unshius Pericarpium(陳皮), Bambusae Caulis in Taeniam(竹茹), Aurantii Immaturus Fructus(枳實), Glycyrrhizae Radix(甘草) |
Ⅲ. 결 과
선정된 22편의 논문의 연도별 분포는 2017년 3편6-8), 2018년 4편9-12), 2019년 4편13-6), 2020년 7편17-23), 2021년 4편24-7)이었다. 또한 선정된 22편의 논문 모두에서 환자들의 평균 나이는 최소 35.4±12.6세에서 최대 64.2±1.7세였다. 질병 이환 기간의 평균값을 언급한 논문은 18편6-9,11,12,16-27)으로, 최장 21.56±5.07일, 최단 3.1±1.2일이였다(Table 1).
1편27)의 연구를 제외한 모든 논문에서 치료기간을 언급하였다. 치료 기간은 최소 10일, 최대 28일이었다.
치료군 중재는 한약 단독 치료 또는 한약과 양방 병행 치료였다. 총 22편 중 3편7,8,21) 에서 치료군 중재로 한약 단독 치료를 시행하였고, 19편6,9-27)에서는 한약과 양방 치료를 병행하였다. 치료군 중재에는 22편의 논문 모두에서 경구 한약 치료를 사용하였고 침, 뜸 등 한약을 제외한 기타 한방 치료는 시행되지 않았다.
총 22편의 논문 중 20편6-13,16-27)의 연구에서는 각 1개씩의 처방을 사용하였고, 2편14,15)의 연구에서는 환자를 변증에 따라 세 가지 처방을 사용하였다(Table 3). 처방명을 언급한 논문은 16편6,7,11-6,19-22,24-7)이었으며 가장 빈용된 처방은 6편6,7,14,20,21,25)의 연구에서 사용된 通竅活血湯加減이었다. Tang6)의 논문에서 사용된 耳聾2號方은 논문에서 通竅活血湯加減方이라고 명시하였다. 그 외로는 清肝通竅湯, 聪耳通窍汤, 益耳通竅湯, 龍膽瀉肝湯, 銀翹散, 四君子湯, 半夏白朮天麻湯, 杞菊地黃湯, 補中益氣湯, 通絡開竅方, 歸脾湯, 潛陽封髓丹, 活血理氣通氣湯, 溫膽湯이 각 1건 처방되었다. 처방명이 동일한 경우에도 연구마다 약재의 가감을 시행하여 약재 구성의 차이는 있었다(Table 3).
처방 중 가장 많이 사용된 약재는 甘草로서 16개(61.5%)의 처방에서 이용되었고, 石菖蒲가 14개(53.8%), 當歸, 柴胡, 桃仁, 川芎이 13개(50%), 紅花, 赤芍藥이 12개(46.2%), 葛根이 10개(38.5%), 丹蔘이 9개(34.6%), 桔梗이 6개(23.0%), 鬱金, 生地黃, 香附子, 陳皮, 黃芪, 枳殼, 澤瀉가 각 5개(19.2%)의 처방에서 이용되었다(Table 5).
본초학적 분류28)에 따르면, 사용된 약재 79개 중 17개(21.5%)가 補益藥에 속하여 가장 많은 비중을 차지하였고, 解表藥이 13개(16.5%), 淸熱藥이 11개(13.9%)였다(Table 4). 《本草學》 교과서에 약재 분류가 명시되지 않은 路路通, 化橘红, 鬼箭羽는 분석에서 제외하였다.
대조군 중재는 22편의 논문 모두에서 서양의학 치료 를 사용하였다. 대조군 중재로는 스테로이드제제을 사용한 논문이 14편9,10,12,13,16-8,20,22-7)으로 가장 많았으며 이 중 2편13,24)는 고실내 스테로이드 주입법, 1편16)은 스테로이드를 귀 뒤에 주입했다. 이외에 혈관확장제 10편6,7,14-5,17-21,26), 비타민제 10편6-10,18,20-2,25), 혈액순환 개선제 7편8,11,13,22-5), 어지럼증 치료제 3편10,11,13), 신경성장인자 3편19,23,24), 항산화제 1편9), 조효소 1편12), 호르몬제 1편14), 신경영양제 1편26), 항응고제 1편26)이 사용되었다.
총 22편의 논문 중 Tang6)의 연구 1편을 제외한 모든 논문에서 총 유효율을 평가 지표로 삼았다. 총 유효율은 [(치유(治癒)+현효(顯效)+유효(有效))건 수/총 건수]×100%로 산출하였으며 총 유효율을 판단하기 위한 항목으로는 순음청력검사상 평균 역치와 임상 증상이 사용되었다. 각 항목들에 대한 호전 평가 기준은 연구 마다 차이가 있었다(Table 2).
Tang6)의 연구에서는 치료 효과지수를 평가 지표로 활용하였으며 [(치료 전 적분-치료 후 적분)/치료후 적분]×100로 산출하였다.
치료 전 평균 역치를 언급한 논문은 14편6-9,13,15-8, 20-2,25,26)이었으나 13편7-9,13,15-8,20-2,25,26)의 논문에서 치료 후 순음청력검사 평균 역치를 언급하여 평가지표로 활용하였다.
-
총 유효율을 평가지표로 사용한 논문 21편 모두 치료군의 총 유효율이 대조군에 비해 통계적으로 유의하게 높았으나(p<0.05) 그 중 Ye13)의 연구에서는 그 결과가 통계적으로 유의하지 않았다(p>0.05).
-
치료 효과지수를 평가 지표로 활용한 Tang6)의 연구에서 치료군의 치료 효과지수가 대조군에 비해 통계적으로 유의하게 높았다(p<0.05).
-
순음청력검사를 평가지표로 활용한 연구에서 치료군의 치료 전 순음청력검사 평균 역치는 최소 40.39±10.57㏈, 최대 74.53±8.96㏈이며 치료 후 순음청력검사 평균 역치는 최소 31.17±4.13㏈, 최대 50.6±19.4㏈였다. 대조군의 치료 전 순음청력검사 평균 역치는 최소 43.84±12.11㏈, 최대 73.48±9.70㏈이며, 치료 후 순음청력검사 평균 역치는 최소 35.75±20.61㏈, 최대 62.2±21.2㏈이다. 치료군의 순음청력검사 평균 역치가 대조군에 비해 통계적으로 유의하게 개선되었다고 보고하였다(p<0.05).
-
치료 전 혈액유변학 지표 측정값을 치료 후와 비교하여 혈액 순환 개선 정도를 평가한 연구 중 Tang6)의 연구에서는 혈액 유변학 지표의 세부 항목 중 활성화부분트롬보플라스틴 시간을 제외하고 프로트롬빈 시간과 트롬빈 시간이 치료군이 대조군보다 유의한 변화를 보였다(p<0.05). Xue12)의 연구에서는 전혈점도, Wang16)의 연구에서는 혈장 점도, 혈소판응집률, 적혈구용적률, 혈장호모시스테인, Qi18)의 연구에서는 적혈구용적률, 피브리노겐, 혈장점도, Fu19)의 연구에서는 적혈구용적률, 피브리노겐, 혈장점도, 전혈점도, Huang25)의 연구에서는 피브리노겐, 혈장점도, 점혈점도를 지표로 사용했고 모든 항목에서 치료군이 대조군보다 유의한 개선을 보였다(p<0.05).
-
혈중 지질과 동맥경화성 혈장지수를 평가 지표로 사용한 Sun20)의 연구에서 치료군이 대조군에 비해 통계적으로 유의한 개선을 보였다(p<0.05).
-
돌발성 난청의 동반 증상 호전 정도를 평가 지표로 활용한 논문 14편6-8,11,13,15,17,19,21-5,27) 중 Tang6)의 연구에서는 난청, 현기증 항목에서 치료군이 대조군보다 유의한 개선을 보였고(p<0.05), 이명은 유의한 개선을 보였으나 통계적으로 유의하지 않았다(p>0.05). Guo21)의 연구에서는 이명은 치료군이 대조군보다 유의한 개선을 보였고(p<0.05), 현기증과 이충만감은 유의한 개선을 보였으나 통계적으로 유의하지 않았다(p>0.05). 나머지 12편의 연구에서는 모든 동반 증상 항목에서 치료군이 대조군에 비해 통계적으로 유의한 호전을 보였다(p<0.05).
Ⅳ. 고 찰
돌발성 난청은 임상에서 드물지 않게 접할 수 있는 귀의 질환으로서 조기에 진단하여 치료를 시작하는 것이 예후의 중요한 인자가 된다. 그리고 스테로이드 요법만이 원인 불명의 돌발성 난청에 대한 효과를 인정받고 있는 실정이다1). 그러나 돌발성 난청 치료 후에도 환자들은 청력 감소로 인한 불편을 지속적으로 호소하는 경우가 많으며 이명, 현기증, 이충만감 등의 동반 증상도 환자의 삶의 질을 떨어뜨린다29). 돌발성 난청 환자의 80%는 이명이 동반되고, 30%는 현기증을 호소한다3). 또한 36%의 환자들은 발병 후 2개월이 지난 시점에서 지속적인 이명을 호소하며 8.7%의 환자가 현기증과 변동성 청력을 호소한다는 보고가 있다29). 그러므로 돌발성 난청 치료에서 청력 수치의 회복과 함께 동반 증상을 개선하는 것이 치료의 요점이 된다.
본 연구에서 대조군 중재로 가장 많이 사용된 서양의학 치료법은 스테로이드 요법이다. 하지만 스테로이드를 경구 투약하거나 정맥 투여 시 위장장애, 안면홍조, 여드름, 불면 등의 부작용이 보고되고 있다30). 이러한 부작용을 줄이기 위해 스테로이드를 고실 내로 직접 주입하는 방법도 있으나 이 방법 역시 이통, 고막 천공, 일시적 현기증 등의 부작용을 일으킬 수 있다1). 그 다음으로 다용된 중재는 혈관 확장제로 혈액의 점도를 낮추어 와우 내 혈류를 개선하고자 사용되었다. 하지만 이는 출혈성 경향 및 과거 뇌출혈 병력이 있는 환자에게는 금기이다2). 또한 대량의 혈관확장제를 사용하더라도 와우 혈류가 증가하지 않았다는 연구 결과도 있다31).
본 연구에서 선정한 총 22편의 논문을 종합하여 분석하였을 때, 한약 단독 치료 또는 한약과 양방 치료를 병행했을 때의 치료 효과가 양방 치료를 단독으로 시행한 대조군보다 높았고 통계적으로 유의했다(Table 2). 또한 동반 증상인 이명, 난청, 이충만감, 현기증, 오심, 구토, 안진 증상도 치료군에서 대조군보다 통계적으로 유의한 개선을 보였다(Table 2). 더불어 치료군과 대조군의 부작용 발생률을 비교한 결과 통계적으로 유의한 차이가 없거나 심각한 부작용이 없었으며, 1편10)에서는 한약과 서양의학 치료를 병행했을 때 서양의학 치료를 단독으로 시행하는 것 보다 부작용 발생률이 통계적으로 유의하게 낮았다. 이로써 한약 단독 치료 및 한약과 양방 치료를 병행하는 것이 양방 단독 치료보다 돌발성 난청에 더 유의한 효과가 있을 것으로 생각된다.
한의학에서는 돌발성 난청을 耳聾의 범주에서 보며 대표적인 병인으로는 風熱, 風濕, 肝火, 痰火, 氣滯瘀血, 腎虛, 氣虛, 心腎不交가 있다4). 총 22편의 논문 중 7편6,7,18,20,21,25,26)의 논문에서 氣滯瘀血을 돌발성 난청의 병인으로 보았고 그 외 肝陽上抗, 肝火上搖, 肝膽實火上搖, 風邪外犯, 瘀血阻絡, 脾氣虛弱, 膽濁中阻, 腎精虧虛, 氣血虧虛, 痰火鬱結이 언급되었다.
6편6,7,14,20,21,25)의 논문에서 通竅活血湯이 사용되었는데, 이는 活血通竅하는 효능이 있어 난청의 한방 변증 중 氣滯血瘀型에 활용할 수 있다32). 연구 내에서 같은 처방이라도 환자의 변증과 증상에 따라 단일 약재를 추가하여 치료의 다양성을 도모하였다.
치료군에서 사용된 약재는 본초학적 분류상 補益藥(21.5%)에 속하는 경우가 가장 많았다. 개별 약재로는 甘草(61.5%)의 빈도가 가장 높았으나 주로 調和諸藥의 의미로서 주로 쓰였다. 그러므로 치료제의 목적으로 가장 많이 사용된 약재는 石菖蒲(53.8%)이고, 當歸, 柴胡, 川芎, 桃仁(50%)이 그 뒤를 이었다28). 石菖蒲는 開竅藥에 해당하여 利濕通竅, 芳香開竅, 活血通竅의 효능이 있고28), 《東醫寶鑑》33)에서는 단방으로 耳聾, 耳痛을 치료한다고 하였다. Li9) 등의 연구는 石菖蒲가 쥐 신경 세포의 세포 사멸을 억제하고 혈장 피브리노겐 함량을 증가시켜 혈액 점도를 감소시킬 수 있다고 하였다. 따라서 石菖蒲의 開竅하는 효능은 현대의학적으로 혈소판 응집을 억제함으로써 와우내 혈류를 개선시키는 기전으로 생각할 수 있다. 또한 Tang6)의 연구에 따르면 補血藥에 해당하는 當歸, 活血去瘀藥에 해당하는 川芎, 桃仁는 혈소판 응집을 억제하고 미세혈관을 확장하며 혈액 점도를 낮춰 내이의 국소 혈액 순환을 개선한다. Wang16)은 當歸의 페룰산(ferulic acid) 성분이 항염증 작용이 있어 내이 염증이 청력을 손상시키는 것을 막는다고 하였다. 한편, 柴胡는 解表藥으로서 疏利經氣, 疏風의 효능이 있고 柴胡 추출물이 염증을 유도한 HMC-1 세포로부터 IL-6와 TNF-α와 같은 염증 관련 물질 분비를 억제하여 항염증 효과가 있다는 연구 결과가 있다34). 그러므로 선정된 논문에서 사용된 주요 약물들은 와우의 혈류 순환을 원활하게 하고, 와우와 청신경의 염증을 감소시켜 돌발성 난청을 완화시킬 수 있을 것으로 생각된다.
객관적인 지표로 혈액유변학 지표들을 측정하여 비교한 논문은 6편6,12,16,18,19,25)이였다. 1편8)의 논문에서 사용된 활성화부분트롬보플라스틴 시간을 제외하고 나머지 논문에서 사용된 프로트롬빈 시간, 트롬빈 시간, 전혈점도, 혈장 점도, 혈소판응집률, 적혈구용적률, 혈장호모시스테인, 피브리노겐은 치료군이 대조군보다 유의한 변화를 보였다. 이는 한약 치료가 혈액유변학 지표를 개선하여 내이의 국소 혈류 순환을 도와 돌발성 난청을 치료할 수 있음을 시사한다.
또한 지질 대사 장애는 와우 유모 세포에 지질을 침착시켜 와우 신경 세포를 손상하는 기전으로 돌발성 난청을 유발할 수 있다20). 선정된 22편의 논문 중 혈중 지질 대사 지표를 평가지표로 활용한 논문은 Sun20)의 연구 1편이었으며 치료군이 대조군보다 치료 후 혈중 지질 대사 측면에서 유의한 개선을 보였다. 이를 통해 한약 치료가 내이 세포의 지질 대사 환경을 개선하여 환자의 청력을 향상시키는 기전으로 돌발성 난청을 치료할 수 있음을 알 수 있다.
본 연구에 포함된 논문은 통일된 평가 항목과 지표를 사용하지 않아 치료의 효과를 일괄적으로 평가하기 어려움이 있다. 또한 총 22편의 논문 중 7편10-2,18-20,25)의 논문을 제외한 15편의 논문에서 무작위 배정 순서를 생성하는 방법에 대한 언급이 없어 통계적 비뚤림의 가능성이 있다.
이러한 한계점에도 불구하고 본 연구는 돌발성 난청의 한의학적 치료에 대한 RCT 논문을 분석한 유일한 연구로 돌발성 난청에서 양방 치료와 한약 치료의 병행이 양방 치료를 단독으로 시행하는 것에 비해 효과가 좋으며, 일부에서는 한약 치료가 양방 단독 치료보다 뛰어난 효과를 보일 수 있음을 제시하였다. 또한 순음청력역치의 개선뿐만 아니라 이명, 난청, 이충만감, 현기증, 오심, 구토와 같은 동반 증상을 개선시킬 수 있다는 근거 자료로써 활용할 수 있다. 향후 돌발성 난청의 치료와 평가에 있어 객관성을 가지기 위해 신뢰도를 가진 통일된 평가 지표가 필요할 것으로 생각되며 국내에서도 질 높은 RCT 연구가 활발히 이루어지길 기대한다.
Ⅴ. 결 론
2개의 중국 데이터베이스에서 검색된 돌발성 난청의 한약 치료 논문들을 분석하여 다음과 같은 결론을 얻었다.
-
총 22편의 논문 중 19편에서 치료군 중재로 한약 치료와 양방 치료를 병행하였고, 3편에서는 한약 단독 치료를 시행하였다. 대조군 중재는 모든 연구에서 양방 치료였다.
-
총 22편의 논문 중 20편의 연구에서는 단일 처방을 사용하였고, 2편의 연구에서는 환자를 변증별로 나누어 세 가지 처방을 사용하였다. 처방명을 언급한 논문은 16편이었으며 빈용된 처방은 6편의 연구에서 사용된 通竅活血湯加減이었다.
-
선정된 논문들에 사용된 한약은 본초학적 목차에 따라 補益藥이 17개(21.5%)로 가장 많이 사용되었다. 그다음으로 解表藥 13개(16.5%), 淸熱藥 11개(13.9%)가 사용되었다. 가장 빈용된 약재는 甘草로서 16개(61.5%)의 처방에서 이용되었고, 石菖蒲가 14개(53.8%), 當歸, 柴胡, 桃仁, 川芎이 각각 13개(50%)개의 처방에서 이용되었다.
-
총 유효율을 평가지표로 사용한 논문 21편 중 1편을 제외한 20편과 치료 효과지수를 평가지표로 사용한 논문 1편에서 한약 단독 치료 또는 한약과 서양의학 치료를 병행했을 때의 치료 효과가 서양의학 치료를 단독으로 시행할 때 보다 효과가 좋음을 밝혔다.
-
치료 전후 순음청력검사상 평균 역치를 평가 기준으로 사용한 13편의 논문 모두에서 치료군의 순음청력검사상 평균 역치가 대조군보다 통계적으로 유효하게 개선되었다. 치료 전후의 혈액 유변학 지표 측정값을 비교하여 혈액 순환 개선 정도를 평가한 6편의 논문 중 1편의 연구에서 사용된 활성화부분트롬보플라스틴 시간을 제외한 그 외 혈액 유변학 지표들은 치료군이 대조군보다 유의한 개선을 보였다(p<0.05). 1편의 논문이 혈중 지질과 동맥경화성 혈장지수를 평가지표로 사용하였고 치료군이 대조군보다 통계적으로 유의한 개선을 보였다(p<0.05).
-
14편의 논문에서 돌발성 난청의 동반 증상이 호전된 정도를 평가지표로 활용하였다. 평가 결과 이명에서 1편, 현기증과 이충만감에서 1편을 제외한 대부분의 논문에서 동반 증상이 유의하게 호전되었다(p<0.05).
-
부작용 발생률을 언급한 9편의 논문 중 5편에서는 치료군과 대조군 간 부작용 발생률이 통계적으로 유의한 차이가 없다고 보고했고(p>0.05), 3편에서는 심각한 부작용은 없다고 보고했다. 1편에서는 치료군에서 대조군보다 부작용 발생률이 통계적으로 유의하게 낮았다(p<0.05).