Ⅰ. 서 론
사시라 함은 한 눈이 어떤 물체를 직시할 때 다른 한 눈이 그것과 다른 방향으로 향하는 것을 말하며1) 시각의 감각계나 운동계에 장애가 있어 양안시선(兩眼視線)이 주시물체와 일치되지 않는 상태를 통틀어 말한다2). 사시는 안근마비의 유무에 따라 마비성 사시와 비마비성 사시로 분류된다. 마비성 사시는 안근이 한 개 혹은 몇 개가 마비되어 시선의 방향에 따라 사시의 정도가 달라지며 안구운동의 제한, 복시, 定位誤認 등의 증세가 나타나므로 非共同性 사시라고 한다. 비마비성 사시는 한쪽 눈의 안구운동에는 이상이 없고 편위도가 주시 방향에 관계없이 항상 일정하기 때문에 共同性 사시라고도 한다3). 한의학에서는 《諸病源候論》에서 최초로 사시질환을 ‘目偏視’라고 언급한 이래로, 通睛, 鬪鷄眼, 雙目通睛, 小兒通睛, 鬪睛, 轆轤轉關, 神珠將反, 瞳神反背, 墮睛, 風引喎斜, 偏視, 天旋, 目仰視, 眼肌麻痹, 視一爲二, 風見偏視 등 여러 가지 명칭으로 질환이 기술되어 왔다4). 한의학 학술지를 통한 사시에 대한 연구는 1992년에 김5)의 논문이 발표된 이래로 2020년까지 지속적으로 이루어져 왔다. 그러나 그 연구의 경향이 주로 증례보고 논문 위주였으며, 아직까지 연구의 경향 내지 동향을 주제로 발표된 논문은 이 등6)의 논문 이외에는 없었다. 해당 분야에서 현재까지 어떠한 연구가 이루어져 왔는지에 대하여 연구하는 작업은, 지금까지의 성과를 객관적으로 바라보고 미래의 계획을 세우는 데 있어서 매우 중요한 일이다. 이에 본 연구는 국내 한의학 학술지에 게재되었던 사시 관련 논문들을 검색 및 수집하고 몇 가지의 기준에 따라 분석하여 지금까지의 연구 상황을 객관적으로 파악하고 앞으로의 사시 질환에 대한 연구에 객관적인 정보를 제공하고자 하였다.
Ⅱ. 연구대상 및 방법
-
1) 검색에 활용한 데이터베이스
-
① 전통의학정보포털(http://oasis.kiom.re.kr)
-
② 대한한방안이비인후피부과학회(http://www.ood.or.kr/)
-
③ RISS(http://www.riss.or.kr/)
-
④ DBpia(http://www.dbpia.co.kr/)
-
⑤ 구글(https://www.google.com/)
-
-
2) 게재 시기 : 1992년 1월 1일 - 2020년 9월 20일 사이에 게재된 논문
-
3) 조사 기간 : 2020년 7월 15일 - 2020년 9월 20일까지 해당 데이터베이스를 검색
-
4) 검색어 : 사시, 사위, 양안시, 시력, 복시, 마비성, 차폐검사, 동안신경 마비, 외전신경 마비
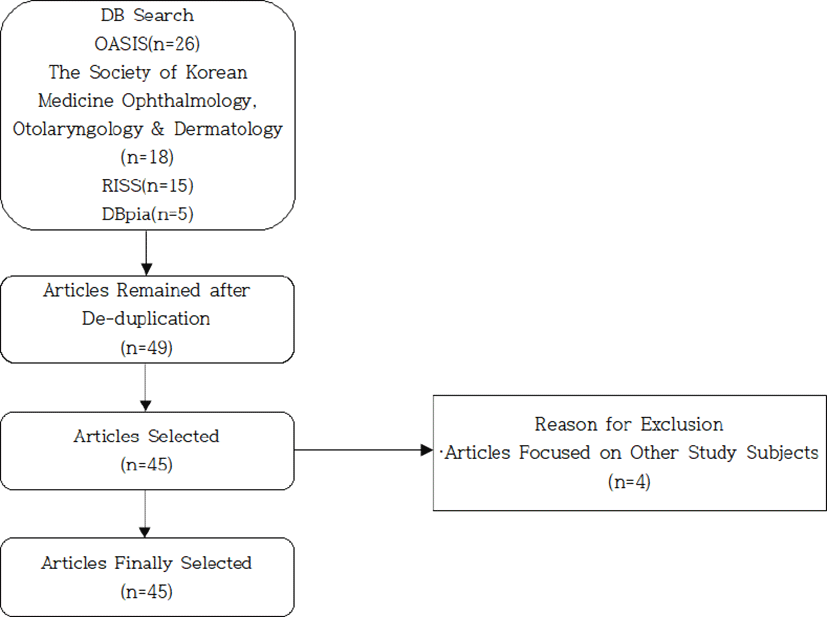
1번의 기준으로 검색하고 2번의 기준으로 수집한 49편의 논문 중에서 다른 연구 분야에 중점을 맞춘 논문 4편을 배제한 45편을 연구대상으로 선정하였다(Fig. 1).
해당 인터넷 사이트에서 검색 후 수집한 총 45편의 논문을 연도별, 학회지별, 저자 수별로 분류하였고, 논문의 종류에 따라 종설, 원저, 증례보고 중 하나로 분류했다. 증례보고 논문은 중추성과 말초성, 마비성과 비마비성, 병변과 관련된 신경, 치료법, 치료 기간 등을 기준으로 분류하였으며 이 중에서 치료 기간은 별도로 표를 만들어서 분석하였다(Table 1-8).
Ⅲ. 연구결과
국내 한의학 학술지에 게재된 사시 관련 논문들의 게재 연도별 논문의 수를 조사했다. 1992년 처음 게재된 이래로 2020년까지 총 45편이 게재되었는데, 2004년에 5편(11.1%)으로 가장 많이 게재되었고, 다음으로 2019년에 4편(8.9%)이 게재되었다(Table 1).
국내 한의학 학술지에 게재된 사시 관련 논문 45편 중, 대한안이비인후피부과학회지에 게재된 논문이 18편으로 전체의 40%를 차지했다. 여기에는 해당 학회지의 구 명칭인 대한외관학회지에 게재된 논문 5편이 포함된다. 다음으로 대한한방내과학회지에 6편(13.3%)이 게재되었고, 동의생리병리학회지와 대한침구학회지, 그리고 대한한방소아과학회지에 각각 4편(8.9%)이 게재되었다(Table 2).
국내 한의학 학술지에 게재된 사시 관련 논문 45편을 저자 수를 기준으로 분류하였을 때, 저자 수는 2인과 3인이 공동 10편(각각 22.2%)으로 가장 많았고, 다음으로 5인이 6편(13.3%)으로 많았다(Table 3).
| Author Number | Article Number | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 | 8.9 |
| 2 | 10 | 22.2 |
| 3 | 10 | 22.2 |
| 4 | 4 | 8.9 |
| 5 | 6 | 13.3 |
| 6 | 3 | 6.7 |
| 7 | 4 | 8.9 |
| 8 | 3 | 6.7 |
| 10 | 1 | 2.2 |
| Total | 45 | 100 |
국내 한의학 학술지에 게재된 사시 관련 논문 45편을 종류별로 분류한 결과, 종설이 2편(4.4%), 원저가 1편(2.2%), 증례보고가 42편(93.3%)이었다(Table 4).
| Type | Number | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Review Article | 2 | 4.4 |
| Original Article | 1 | 2.2 |
| Case Report | 42 | 93.3 |
| Total | 45 | 100 |
성별을 기준으로 여자가 38례(46.9%), 남자가 43례(53.1%)이었다(Table 5). 연령을 기준으로는 60대가 21례(25.9%)로 가장 많았고, 30대가 14례(17.3%), 10대 미만이 12례(14.8%)로 그 다음이었다(Table 6).
| Age | Number | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0-9 | 12 | 14.8 |
| 10-19 | 5 | 6.2 |
| 20-29 | 3 | 3.7 |
| 30-39 | 14 | 17.3 |
| 40-49 | 9 | 11.1 |
| 50-59 | 10 | 12.3 |
| 60-69 | 21 | 25.9 |
| 70-79 | 6 | 7.4 |
| 80-89 | 1 | 1.2 |
| Total | 81 | 100 |
증례보고 논문 42편 중에서 35편(83.3%)이 말초성 사시에 대한 논문이었고, 7편(16.7%)이 중추성 사시에 대한 논문이었다. 42편 전부 마비성 사시에 대한 논문이었는데, 이 중 1편은 비마비성 사시에 대한 증례를 함께 보고했다(Table 5).
마비성 사시 유발과 관련된 뇌신경으로 분류한 결과, 동안신경이 관련된 경우가 19편(45.2%), 외전신경이 관련된 경우가 12편(29%), 그리고 두 신경이 다 관련된 경우가 3편(7.1%)이었다. 관련 뇌신경이 논문에 명시되어있지 않은 경우는 8편(19%)이었다(Table 5).
발병 후 한의 치료를 받기까지 걸린 기간은 10일 미만이 20례(24.7%)로 가장 많았고 10일부터 19일까지가 21례(25.9%)로 그 다음이었다(Table 7). 평균 치료 기간으로 분류한 결과, 30일 이하인 경우가 15편(35.7%)으로 가장 많았고, 다음으로 31일 이상 60일 이하인 경우가 13편(31%)으로 많았다. 치료 기간이 불명확한 경우는 2편(4.8%)이었다(Table 8).
| Treatment Period (day) | Number of Article | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1-30 | 15 | 35.7 |
| 31-60 | 13 | 31 |
| 61-90 | 6 | 14.3 |
| 91-120 | 4 | 9.5 |
| 121-150 | 1 | 2.4 |
| 151-180 | 0 | 0 |
| 181-210 | 1 | 2.4 |
| Uncertainty | 2 | 4.8 |
| Total | 42 | 100 |
치료의 병행 여부를 기준으로 양의 치료와 병행한 경우가 9례였고 양의 치료는 전혀 하지 않고 한의 치료만을 단독으로 시행한 경우가 72례이었다(Table 5). 사용된 치료 방법으로 분류한 결과, 침 치료가 37편(88.1%)이었고 한약 치료가 36편(85.7%)이었다. 전침 치료를 침 치료에 포함한다면, 42편 전부에 침 치료가 사용된 것으로 볼 수 있다(Table 5). 42편의 증례보고 중에서 한약을 처방한 논문이 36편(85.7%)이었고 한약을 전혀 처방하지 않은 논문이 6편(14.3%)이었다(Table 5).
Ⅳ. 고 찰
사시(strabismus)란 안구의 비정상배열을 일컫는다7). 사시는 사시(heterotropia)와 사위(heterophoria)로 나눈다. 사시는 한쪽 눈의 시선이 항상 편위되어 있어 양안시가 불가능하다. 사위는 양안시가 가능하나 한 눈을 가려서 융합을 방해할 때, 피로할 때, 아침에 일어났을 때, 열이 날 때, 공상을 할 때 등 융합이 약해지는 상태에 있을 때는 사시를 보일 수도 있다8). 사시는 인 구의 2-4%에서 발병한다9). 사시의 위험요인은 가족력, 저체중 출생으로 의심되지만 확실하지는 않다. 각막상처, 백내장, 심한 안검 하수, 장기간 지속된 유리체 출혈로 인한 시야 손상·근육 이상·원시·뇌손상·부등시·약시·양안 융합의 손상 등으로 인해 사시가 발생할 수 있다10). 사시는 발생 원인에 따라 중추성 사시와 말초성 사시로 나눌 수 있다. 중추성 사시는 뇌의 병변이나 내상과 같은, 뇌 자체의 문제로 인해 발생하는 사시이다. 말초성 사시는 뇌신경의 문제로 인해 발생하는 사시이다3). 사시는 신경 마비 여부에 따라 마비성 사시와 비마비성 사시, 주시 방향에 따라 내사시, 외사시, 상사시, 하사시로 분류한다. 또한 그 나타나는 상태에 따라서 항시성, 간헐성, 교대성이 있고 조절성, 비조절성으로 나눌 수 있다11). 마비성 사시는 안구의 위치에 따라 편위도가 달라지는데 신경-근육 기전에 의한 운동기능의 완전 또는 부분 장애로 생기며 병소는 근육, 신경-근육 접합부, 말초신경, 신경핵 또는 상부 신경회로가 될 수 있다. 그 중 제 3번, 4번, 6번 뇌신경의 마비는 안과 영역에서 마비성사시를 일으키는 주요 원인이며 두개내의 질환을 진단할 수 있는 단서가 된다12). 말초신경으로 인한 외안근 마비는 주로 제6신경 외전신경(abducens nerve)이 가장 흔하게 나타나고, 제3신경 동안신경(oculomotor nerve), 제4신경 활차신경(trochlear nerve) 순으로 발생한다13). 동안신경(oculomotor nerve)은 중뇌 대뇌각의 내측에서 나와 해면정맥동의 상벽을 따라 앞으로 가서 상안와열을 활차신경, 안신경, 외전신경과 같이 지나서 외측직근과 상사근을 제외한 외래안근과 상안검거근에 분포하는 운동성 신경이다. 동안신경부핵 또는 Edinger-Westphal핵에서 나온 부교감성 신경섬유가 있으며, 모양체신경절(ciliary ganglion)을 거쳐 안구내부의 평활근 즉 모양체근, 동공괄약근에 분포한다14). 동안신경마비는 마비가 되면 지배를 받는 근육들의 단독적인 근육마비는 드물며 몇 개의 근육들이 동시에 마비되어서 나타나는 경우가 많다. 내직근, 상·하직근, 하사근마비로 인해 외전, 내전, 상전, 하전장애 등이 발생되어 안구가 외하방으로 편위된다. 안검거근의 마비로 안검 하수(blepharoptosis)가 현저하게 나타나며 경미한 안구 돌출도 발생되기도 한다13). 외전신경(abducens nerve)은 교와 연수사이에서 나와 내경동맥의 외측을 지나 상안와열에서 안와로 들어와 안구를 외전시키는 외측직근에 분포한다. 안구 운동에 관여하는 3개의 신경 중 그 경로가 길고 손상받기 쉬운 신경이다14). 외전신경마비는 외직근의 마비로 인해 외전 장애가 나타나고, 길항근인 내직근 작용으로 내사시가 나타난다. 상하방향의 편위는 없고 외전이 제한되며 수평성의 복시가 일어나고, 복시를 줄이거나 없애기 위해 안면은 마비안의 방향으로 회전시킨다. 마비안을 외전시키면 복시가 현저해지고, 내전시키면 소실되거나 감소된다13). 사시는 한의학에서 《諸病源候論》에 최초로 기재되었으며 후세에는 ‘目偏視風引’, ‘風引喎斜’, ‘偏視’ 등으로 호칭되었다. 또한 사시의 정도와 방향에 따라서 복시를 동반하기 때문에, 문헌상으로는 ‘視一爲二’, ‘神珠將反’, ‘瞳神反背’, ‘雙目通睛’ 등에 포함되어 있는 경우도 있다. 대개 원인으로 風邪中絡, 痰濕阻絡, 風熱上攻, 肝風內動, 瘀血阻滯, 先天不足 등을 들 수 있다15). 마비성 사시는 한의학에서 병명이 일정치 않으며 眼肌麻痹라고도 하며 眼位偏斜 위주인 것을 ‘目偏視’, ‘神珠將反’, ‘瞳神反背’, ‘墮睛’, ‘目仰視’라 칭하고 복시 위주인 것을 ‘視一爲二’라 한다16).
본 연구에서는 1992년부터 2020년까지 국내 한의학 학술지에 게재되었던 총 45편의 논문을 수집하여 분석하였다(Fig. 1). 1992년에 처음 사시 관련 논문이 게재된 이래, 2020년까지 매년 1편에서 5편의 논문이 게재되었고 한 편도 게재되지 않은 해가 없이 꾸준히 게재되어 왔음을 알 수 있다(Table 1). 게재 연도별 논문의 수에서는 2004년에 5편(11.1%)으로 가장 많았고, 2019년에 4편(8.9%)이었다. 또한 2003년부터 2010년까지 8년 동안 전체 45편 중 20편(44.4%)이 게재되어, 이 시기에 한의학계에서 사시에 대한 연구가 활발히 이루어졌음을 짐작할 수 있다(Table 1). 학회지별로는 대한한방안이비인후피부과학회지에 게재된 논문이 18편으로 전체의 40%를 차지했다. 이 결과로 볼 때 사시 연구에 있어서 대한한방안이비인후피부과학회지에서 가장 활발히 연구가 수행되었음을 알 수 있다. 다만 중추성 사시의 경우에는 대한한방내과학회지에 2편, 대한한방안이비인후피부과학회지에 2편, 대전대학교 대학원 논문집에 1편, 대한침구학회지에 1편, 동의생리병리학회지에 1편으로 다양하게 게재되었음을 알 수 있다(Table 2). 저자 수에 따른 논문의 분류는 2인과 3인이 공동 10편(각각 22.2%)으로 가장 많았다(Table 3). 2-3인의 공동 연구가 일반적이고, 그 이상의 인원이나 단독 연구는 비교적 적은 것으로 보인다. 논문의 저자 수를 분석하는 이유는 프로젝트 참가를 통한 공동연구 여부를 확인하는 의미가 있다. 2004년 Week 등17)은 1980년부터 2000년까지 JAMA, Annals of Internal Medicine, Archives of Internal Medicine, New England Journal of Medicine 등에 실린 논문의 저자 수를 분석하여 1980년 4.5명에서 2000년 6.9명으로 증가되는 양상을 확인한 바 있다. 45편의 논문을 권 등18)이 사용한 방식을 기반으로 하여 종설, 원저, 증례보고의 세 가지 범주로 나누었는데, 종설이 2편(4.4%), 원저가 1편(2.2%), 증례보고가 42편(93.3%)이었다(Table 4). 또한 이 42편의 논문이 전부 마비성 사시에 대한 논문이었고 한 편만이 마비성 사시와 비마비성 사시를 다룬 논문이었는데 이를 종합하면 현재 한의학계에서는 ‘마비성 사시에 대한 증례보고 논문’이 주를 이룸을 알 수 있다. 증례보고 논문에는 총 81례의 환자 치료에 대한 증례가 있었으며, 그 중에서 여자가 38례(46.9%), 남자가 43례(53.1%)이었다(Table 5). 남자가 여자보다 5례가 많았지만 제한된 증례보고에서의 숫자이며 큰 의미를 두기는 힘들 것으로 보인다. 연령을 기준으로 보았을 때는 60대가 21례(25.9%)로 가장 많았으나 대부분의 연령에 고르게 분포하는 편이었다(Table 6). 특히 10대 미만이 12례(14.8%)로 어린 나이에도 마비성 사시가 발병하는 경우가 있음을 알 수 있었다. 증례보고 논문 42편에서 사시의 종류를 말초성과 중추성으로 나누어 보았을 때, 말초성 사시에 대한 논문이 35편(83.3%)이었고, 중추성 사시에 대한 논문이 7편(16.7%)이었다(Table 5). 중추성 사시 관련 논문들 중에서 김 등19), 정 등20), 이 등21), 김 등22)의 경우 모두 동안신경과 관련된 내용이었고 나머지 세 편은 어느 신경과 관련이 있는지 언급이 되어 있지 않았다. 즉, 7편 중 4편이 동안신경의 이상과 관련된 논문이었다. 발병 후 한의 치료를 받기까지 걸린 기간은 10일 미만이 20례(24.7%), 10일부터 19일까지가 21례(25.9%)로 발병 후 19일 이내에 치료를 받은 경우가 41례(50.6%)로 절반보다 약간 높았다(Table 7). 이를 한의 치료만을 단독으로 받은 경우가 72례(88.9%)인 점과 함께 본다면(Table 5), 마비성 사시의 발병 초기에 한의 치료가 환자들에게 상당히 신뢰를 받고 있음을 짐작할 수 있다. 증례보고에서 사용된 치료 방법은 침 치료가 37편(88.1%)이었고 한약 치료가 36편(85.7%)이었으며 전침요법이 사용된 경우가 10편(23.8%)이었다(Table 5). 전침요법은 동양의학의 침 치료와 현대과학기술의 결합에 의하여 발전된 침구 치료방법의 하나로 최근에 임상에서 다양하게 응용되고 있다. 전침요법은 자극요건에 따라 치료효과에 차이가 있는 것으로 알려져 있고, 일반적으로 교류전류가 전침요법에 적합한 전류이며, 단속파 소밀파는 통증질환에 사용하고 연속파는 주로 마비질환에 치료에 사용한다고 알려져 있다23). 증례보고에서 치료기간은 30일 이내인 경우가 15편(35.7%)이었고 90일 이내에 치료가 끝난 경우가 모두 34편(81%)인 것으로 보아 대부분의 증례보고에서 3달 이내에 치료가 끝났음을 알 수 있었다. 다만, 91일 이상의 기간이 소요된 경우도 6편(14.3%)에 달하여 치료에 3달 이상의 기간이 소요될 수 있음을 감안해야 할 것이다(Table 8). 이상과 같이 국내 한의학 학술지에 게재된 사시 관련 논문들을 분석한 결과, 국내 한의학계에서 사시에 대한 연구는 마비성 사시와 관련된 증례보고 위주로 이루어져 왔다고 할 수 있다. 종설과 원저의 비중이 낮은 점이 아쉬움이 남으며, 이러한 연구의 편중은 앞으로 보완되어야 할 과제로 보인다. 또한 중추성 사시의 경우 어떤 뇌신경과 관련이 있는지 언급되지 않은 경우가 3편이었고 말초성 사시의 경우 어떤 뇌신경에 문제가 있는지 언급되지 않은 경우가 5편이었다. 이는 임상적인 어려움 때문이라고 추정이 되지만 정확한 연구와 정보 전달을 위해서는 분류하고 명시할 필요가 있다. 증례보고에서 치료기간을 언급하지 않은 경우가 2편이었는데, 증례보고의 정확성을 기하기 위해서는 치료 시작 및 종료 일자를 표기하는 것이 중요할 것이다. 비마비성 사시의 경우 편위도가 일정불변하고 한쪽 눈의 안구운동에는 아무런 이상이 없으며 교대성 사시, 간헐성 사시와 같이 다양한 형태로 증상이 나타나므로 상대적으로 진단이 쉬운 마비성 사시에 대한 연구가 더 많이 되었을 가능성이 있다11). 또한 한의 치료가 마비 질환에 대하여 효과가 있다는 국민들의 인식으로 인하여 마비성 사시 환자들이 치료를 받는 경우가 많아서 이에 연구가 집중되었을 가능성이 있다. 이 두 가능성은 추후에 좀 더 연구를 해야 할 부분이라고 생각한다. 앞으로 사시와 관련된 연구는 비마비성 사시에 중점을 두고, 종설과 원저 논문들로 수행 과정에 대한 충분한 이론적 근거를 확보한 후에 미리 세부적인 계획을 세워서 임상연구를 수행하는 것을 목표로 나아가야 할 것이다.
Ⅴ. 결 론
국내 한의학 학술지에 게재된 사시 관련 논문 45편을 분석한 결과, 다음과 같은 결론을 얻었다.
-
게재 연도별 논문의 수는 2004년이 5편(11.1%)으로 가장 많았다.
-
학회지별 논문의 수는 대한한방안이비인후피부과학회지가 18편(40%)으로 가장 많았다.
-
저자 수에 따른 논문의 분류는 2인 및 3인이 공동 10편(각각 22.2%)으로 가장 많았다.
-
45편의 논문 중 종설이 2편, 원저가 1편, 증례보고가 42편이었다.
-
증례보고 논문 42편 전부 마비성 사시에 대한 논문이었고, 이 중 1편은 비마비성 사시에 대한 증례를 함께 보고했다.
-
증례보고 논문에서 말초성 사시에 대한 논문이 35편(83.3%)이었고, 중추성 사시에 대한 논문이 7편(16.7%)이었다.
-
증례보고 논문에서 동안신경과 관련된 논문이 19편(45.2%), 외전신경과 관련된 논문이 12편(28.6%), 그리고 두 신경 모두 관련된 논문이 3편(7.1%)이었다.
-
증례보고 논문에서 발병 후 한의 치료를 받기까지 걸린 기간은 19일 이내가 41례(50.6%)이었다.
-
증례보고 논문에서 양의 치료는 전혀 하지 않고 한의 치료만을 단독으로 시행한 경우가 72례(88.9%)이었다.
-
증례보고 논문에서 치료법은 침 치료가 37편(88.1%)이었고 한약 치료가 36편(85.7%)이었다.
-
증례보고 논문에서 치료 기간은 30일 이하인 경우가 15편(35.7%)으로 가장 많았다.
현재 한의학계에서 사시 관련 연구는 주로 증례보고 위주로 이루어지고 있고, 종설과 원저 논문의 발표가 미흡하다. 사시 연구의 다양성을 위하여, 종설과 원저 논문의 발표가 더 활발하게 이루어져야 할 것으로 보인다. 그리고 마비성 사시에 편중된 연구 경향을 볼 때, 앞으로 비마비성 사시 환자를 대상으로 한 치료와 연구도 활발히 이루어져야 할 것이다. 또한 증례보고에서는 정확한 연구와 정보 전달을 위해서 사시의 양상과 치료 기간에 대하여 분명히 명시해야 할 것이다.