Ⅰ. 서 론
대상포진(Herpes zoster, Shingles)은 수두 감염 또는 수두 예방접종에 의해 감각신경절에 잠복되어있던 Varicella zoster 바이러스(VZV)의 재활성화에 의해 발생하는 감염성 피부질환이다1). 해당 감각 신경절에 지배되는 피부 분절을 따라 군집성의 수포 발진이 편측으로 나타나는 것이 특징으로 발진이 발생하기 4~5일 전부터 해당 부위에 소양감이나 다양한 양상의 통증이 발생한다. 어느 부위에나 발생할 수 있으나 일반적으로 흉추신경절에서 가장 많으며 뇌신경(삼차신경), 경추신경, 요추 · 천추신경 순으로 호발한다.
한의학에서는 隋代 巢元方의 《諸病源候論·瘡病諸候甑帶瘡候》에 “甑帶瘡者, 纏腰生, 此亦風濕博於血氣所生, 狀如甑帶, 因以寫名”이라고 최초로 기록된 이래 발병부위와 임상표현에 의거해 纏腰火丹, 蛇串瘡, 火帶瘡 등의 다양한 이름으로 기록되어 왔다2). 원인으로 情志內傷로 인한 肝經火盛, 脾失健運으로 인한 濕熱搏結, 年老體虛 등이 제시되며3), 원인에 따라 한약치료와 침구치료를 응용한다.
대상포진의 급성기 치료 목표는 통증의 억제, 바이러스의 확산과 이차 감염 억제, 포진후 동통 등의 합병증 예방 및 최소화이다4). 서양의학적 표준 치료법은 항바이러스제의 투여로, 발진이 발생하고 72시간 이내에 경구 투여하는 것이 원칙이며 통증의 조절이 어려운 경우 경구스테로이드제, 진통소염제, 항경련제, 항우울제 등을 병용한다5). 그러나 발진 시작 72시간 이후 항바이러스제의 효과는 불분명하며 50세 이하의 건강한 환자에서는 항바이러스제 치료의 필요성이 적다는 주장도 있는 등 현재까지 확실한 치료법은 없으며6), 한 연구에서는 실제 임상 현장에서 약물 투여 시 그 효과에 대한 만족도가 부작용이나 편의성에 비해 떨어지는 것으로 보고되기도 하였다7).
현재까지 국외에서 몇몇 무작위 대조군 연구를 통해 침구치료, 부항요법이 급성기 대상포진의 치료와 포진후 신경통(Post Herpetic Neuralgia, PHN) 예방에 있어 잠재적 효과를 가지며, 일부 연구에서는 침 단독치료가 항바이러스제 투여와 유사하거나 더 우수한 효과를 보인다는 보고들이 있어왔다8-11). 그러나 아직 국내에서의 대상포진 치료에 대하여 종합적으로 논해진 적 없으며 특히 대상포진의 한약치료에 관한 고찰은 없었다. 이에 본 연구에서는 국내 한의학 학술지에 보고된 임상 증례 논문을 통해 국내 임상 현장에서의 급성기 대상포진 한방 치료 동향을 분석하고 향후 대상포진의 한의학적 치료에 대한 연구의 방향에 기여하고자 하였다.
Ⅱ. 연구 대상 및 방법
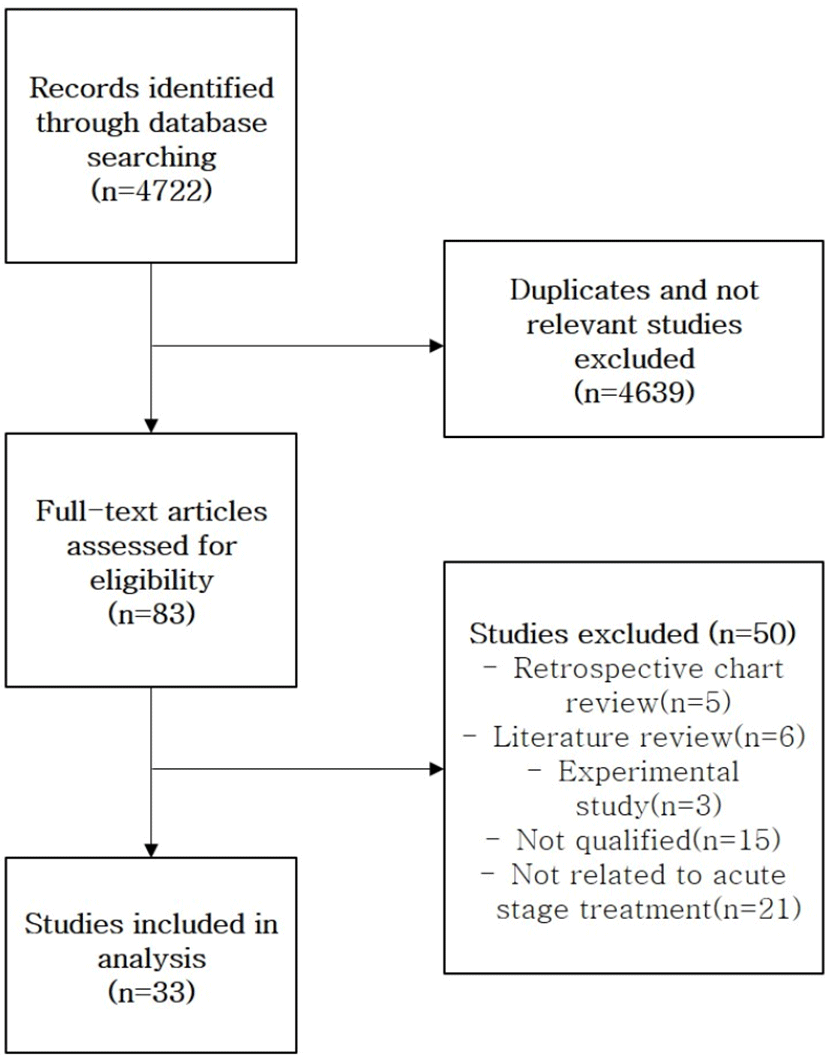
본 연구에서는 전통의학정보포털(Oriental Medicine Advanced Searching Integrated System, OASIS), 한국전통지식포털(Korean Traditional Knowledge Portal, KTKP), 학술연구정보서비스(Research Infor- mation Sharing Service, RISS), 국가과학기술정보센터(National Discovery for Science Leader, NDSL), 한국학술정보(Korean studies Information Service System, KISS)의 총 5개 검색 엔진을 이용하여 ‘대상포진’, 'Herpes zoster', 'Ramsey Hunt'의 키워드로 대상포진 급성기의 한의학적 치료에 대한 증례 보고 문헌을 검색하였다(검색일 : 2019.12.16~2019.12.20). 논문의 출간일은 제한을 두지 않았으며, 제목과 초록에 근거하여 한방 치료에 대한 내용을 포함하고 있는 논문을 선별 후 중복되는 논문을 배제하였다. 일반적으로 피부 발진이 존재하는 시기를 대상포진의 급성기로 정의하며, 대체로 발진이 발생하고 1달째까지를 의미한다12-14). 본 연구에서는 Dworkin 등의 제안12)에 따라 30일을 급성기의 기준으로 삼았다. 논문의 원문을 확인하여 포진후 동통이나 내원 시점이 발병일로부터 30일 이후인 경우 등 급성기 치료에 관한 내용을 포함하지 않은 논문 21편과 각 증례에 대한 치료 내용이 충분히 기술되지 않아 분석이 어려운 차트리뷰 논문 5편, 문헌고찰 6편, 실험 논문 3편, 증례보고 논문으로서의 적절한 형식을 갖추지 못한 논문 15편을 제외하여 최종적으로 33편을 선정하였다(Fig. 1).
선정된 논문을 분석 시 한 논문 내에 여러 건의 증례가 있거나 치료기간이 긴 경우 급성기 치료 방법만 분석에 포함하였고, 대상포진으로 인해 유발된 증상 이외 기타 증상을 치료하기 위해 시행된 방법은 분석에서 제외하였다.
대상포진의 임상 양상은 발병 부위에 따라 얼굴을 제외한 부위에 발생한 경우 범발성 대상포진(Herpes zoster genralisatus), 얼굴에 발생한 경우 안면 대상포진(Facial Herpes zoster)으로 구분하였으며, 이 중 눈을 침범한 경우 안구대상포진(Herpes zoster ophthalmicus)으로 구분하였다. Ramsay Hunt syndrome은 따로 분류하였으며 논문에서 진단명을 명확히 언급한 경우 해당 진단명으로, 그렇지 않은 경우 원문을 확인하여 기재된 환자의 증상 또는 사진을 통하여 분류하였다. 한약 처방을 분석 시 급성기인 30일 이내에 투약된 처방만 분석 대상에 포함하였으며, 사용된 빈도를 분석 시에는 한 증례에서 동일한 처방이 여러 차례 사용된 것이나 일부 약재만을 가감한 경우 중복하여 계산하지 않았고 최초로 사용한 처방의 구성을 분석 대상으로 삼았다. 사용 본초 분석 시 논문 내에 처방 구성 약물이 정확하게 명시되지 않은 경우에는 분석 대상에서 제외하였다.
Ⅲ. 결 과
성별과 연령 분포는 Table 1과 같았으며 대상포진의 유형 및 발병선행요인은 Table 2와 같았다.
| Male | Female | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| <10 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10~19 | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| 20~29 | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| 30~39 | 1 | 4 | 5 |
| 40~49 | 3 | 3 | 6 |
| 50~59 | 3 | 3 | 6 |
| 60~69 | 6 | 4 | 10 |
| >70 | 2 | 9 | 11 |
| Total | 21 | 23 | 44 |
급성기 대상포진의 치료를 위해 시행된 한방 치료 방법은 Table 3과 같았다. 전침치료의 경우 범발성 대상포진의 해당 분절 협척혈에 적용한 1례를 제외하고는 모두 Ramsay Hunt syndrome 증례에 해당하였다. 외용 한약 요법은 총 4례에서 우방자 전탕액이 2회, 지양 정(止痒靜), 일효산(一效散)이 각 1회씩 사용되었다. 매선요법은 Ramsay Hunt syndrome의 치료를 위한 논문 1편에 포함된 증례 4명에서 시행되었다.
30편의 논문, 41례에서 침 치료를 병행하였고 총 65개의 혈위가 사용되었는데 5회 이상 사용된 혈위는 Table 4와 같았다. 범발성 대상포진과 안면 대상포진, Ramsay Hunt syndrome 모두에서 사용된 혈위로는 LI4(合谷), LR3(太衝), ST36(足三里), GB20(風池)가 있었다.
-
① 복합처방 분석
전체 논문 중 29편에서 한약 치료를 시행하였으며 모든 증례에서 단미가 아닌 복합처방을 사용하였다(Table 5). 총 39명의 증례에서 35개의 처방이 사용되었으며 龍膽瀉肝湯이 10회(25.6%)로 가장 많이 사용되었고 理氣祛風散이 8회(20.5%)로 뒤이었는데, 理氣祛風散은 모두 Ramsay Hunt syndrome에서 사용되었다.
-
② 복합처방에 사용된 단미 분석
원문에 상세 약물 구성이 기재되어 있는 39개의 복합처방에서 115개의 본초가 사용되었는데 이를 본초학교과서15) 기준으로 분류한 결과는 Table 6과 같았다. 용량이 기재되어 있지 않은 3개의 처방과 모든 약재가 동량으로 사용되어 君藥16)을 판별하기 어려운 1개의 처방을 제외하고 각 처방에 사용된 君藥의 빈도는 Table 6과 같으며, 5회 이상 다빈도로 사용된 본초는 Table 7과 같았다.
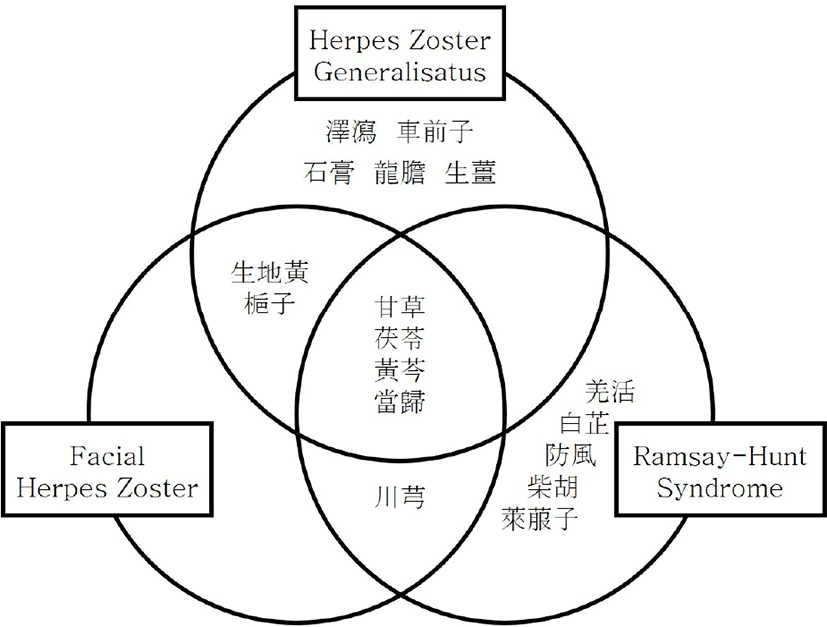
대상포진의 임상 분류별로 사용 빈도 상위 10%를 분석 시 모든 분류에서 甘草, 茯苓, 黃芩, 當歸가, 범발성 대상포진과 안면 대상포진에서는 生地黃, 梔子가, 안면 대상포진과 Ramsay Hunt syndrome에서 川芎이 공통적으로 많이 사용되었다. 澤瀉, 車前子, 石膏, 龍膽, 生薑은 범발성 대상포진에서, 羌活, 白芷, 防風, 柴胡, 萊菔子는 Ramsay Hunt syndrome에서 상위 빈도를 차지하였다(Fig. 2).
모든 논문에서 의사의 진찰 결과를 서술식으로 평가하였다. 전체 대상 논문 33편 중 20편에서 피부병변의 변화를 평가하였는데, 이 중 사진을 통해 피부 병변의 변화를 평가한 것은 7편이었다. Ramsay Hunt syndrome의 경우 총 15편 중 4편에서만 피부 병변의 변화를 기록 · 평가하였다.
통증의 평가도구로는 Visual Analogue Scale(VAS)를 사용한 경우가 14편으로 가장 많았고, Numeric Rating Scale(NRS)를 사용한 경우가 3편이었다. 이외 Pain Rating Score(PRS)와 Verval Rating Scale (VRS), Neuropathy Pain Scale(NPS), Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire(SF-MPQ)가 각 1편에서 사용되었다.
Ramsay Hunt syndrome 증례 보고 15편 중 12편에서 안면마비의 회복 정도를 평가하기 위하여 평가도구를 사용하였다. House Brackmann grade(HB grade)가 9편에서 사용되어 가장 빈도가 높았으며 Yanagihara scale이 5편, FEMA grading system과 Sunnybrook facial grading system(SFGS)이 각 1편에서 이용되었다. 1편에서는 마비의 정도를 5단계로 평가한 자체 평가도구를 이용하였다.
객관적 검사를 평가방법으로 사용한 논문은 Ramsay Hunt syndrome 환자 증례 2편이 있었는데 1편에서는 예후파악을 위하여 적외선체열검사(Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging, DITI)를, 1편에서는 만성 간염환자에서 한약치료의 안전성을 함께 확인하기 위하여 혈액검사(LFT)를 시행하였다.
33편의 논문에 수록된 44례 모두에서 한방치료에 의해 발진의 소실이나 통증의 감소 등 대상포진 증상의 호전(Appendix 1.)을 확인하였으나 단순 전후비교로 논문 당 증례의 수가 1~4례로 적어 통계적 유의성은 확인할 수 없었다.
치료 종료 후 추적조사를 시행한 논문은 총 6편으로 3편은 안구 대상포진 증례, 3편은 범발성 대상포진 증례 논문이었다. 이 중 1편은 범발성 대상포진 환자에서 전침의 즉시 진통효과를 살핀 증례로 추적관찰을 통해 후유증이 남지 않았음을 확인하였으나 한방 치료와 대상포진 후 회복과의 연관성을 파악하기는 어려웠다. 나머지 5편 중 3편은 치료 종결 후 추적조사를 통해 후유증이 남지 않았음을 확인하였고, 2편 중 1편에서는 피로 시 가벼운 이상감각과 가려움이 발생함을, 나머지 1편에서는 안구 대상포진 후유증으로 인한 시력 저하와 이상감각, 따끔거리는 양상의 포진후 동통이 잔존함을 확인하였다.
Ⅳ. 고 찰
본 연구에서는 5가지 국내 데이터베이스를 통해 2019.12까지 발행된 급성기 대상포진 한방 치료에 대한 임상 보고를 종합 · 분석하였다. 총 33건의 논문에서 44례의 증례가 보고되었는데 남성 21명, 여성 23명으로 여성의 증례수가 더 많았으며, 전체 증례 중 50대 이상이 남성 11명(52.4%), 여성16명(69.6%)로 과반수를 차지하였다. 2009-2014년도의 건강보험심사평가원 자료를 이용한 역학 연구17)에서 보고한 국내 대상포진의 발병률이 1000인년당 10.4명(남성 8.3명, 여성 12.6명)으로 여성에서 더 많고, 50대에서 발병률이 급증하여(17.4명) 60대에서 가장 발병률이 높았던(22.4명) 것과 유사한 결과라고 할 수 있다.
발생 부위별 분류에 따른 대상포진의 유형으로는 Ramsay Hunt syndrome의 증례가 20건(45.5%)으로 가장 많았다. 이는 일반적으로 흉부(55%), 뇌신경(20%, 삼차신경에서 다발), 요추신경(15%), 천골신경(5%)의 순으로 호발한다고 알려져 있는 것4)과는 상이한 결과인데, 안면마비가 비교적 한방 의존도가 높은 질환으로 내원 빈도가 높으면서18,19) 특히 Ramsay Hunt syndrome으로 인한 경우 후유증이 눈으로 뚜렷하게 보이나 완치율이 매우 낮아20.21) 초기 치료에 적극적인 경우가 많은 것이 일정 부분 기여하였을 것으로 생각된다. 범발성 대상포진 16건 중에서는 흉부를 침범한 경우가 11건(68.8%)으로 기존에 보고된바와 유사한 경향을 보였다.
급성기 대상포진의 한의학적 치료에 있어 침 치료와 한약 치료가 주된 방법으로 활용되고 있었다. 많이 언급된 혈위로는 ST4(地倉), TE17(翳風), ST6(頰車), TE23(絲竹空), LI4(合谷), BL2(攢竹), GB14(陽白), ST36(足三里), LR3(太衝), GB20(風池), GB21(肩井), CV24(承漿), LI20(迎香), ST2(四白) 등이 있었는데, Ramsay Hunt syndrome의 증례 논문에서 침치료에 관한 언급이 많아 안면마비 치료를 위한 근위 혈자리들이 상위를 차지하고 있었다. LI4(合谷), LR3(太衝), ST36(足三里), GB20(風池)는 모든 분류의 대상포진에서 1회 이상 언급이 되었다. LI4(合谷)은 手陽明大腸經의 原穴로 鎭靜止痛 通經活絡 淸熱解表하는 효능이 있어 습윤성 피부질환에 다용되는 혈위로22) 통증 조절 효과가 뛰어나 침술 마취에도 빈번히 사용된다23-25). LR3(太衝)은 足厥陰肝經의 原穴이면서 兪穴로 平肝息風 淸熱利濕 通絡止痛하는 효능이 있어 肝經의 濕熱을 주된 병리로 하는3) 대상포진의 치료에 효과를 보일것으로 생각되며, 실험연구를 통해 통증 조절과 신경 재생효과가 보고되어 있다26). 또한 LI4(合谷)와 LR3(太衝)은 배오되어(四關穴) 陰陽相交를 통해 鎭靜開竅 祛風止痛 氣血調整등의 효과를 나타내므로27) 급성기 포진으로 인한 통증의 조절에 상승효과를 기대할 수 있다. ST36(足三里)는 足陽明胃經의 合穴이면서 六腑下合穴로 生發胃氣 燥化脾濕하고, GB20(風池)는 少陽經의 交會穴로 平肝熄風 祛風解毒 通利官竅하는 효능을 가지는데 두 혈위는 모두 다수의 실험 및 임상연구를 통해 항염효과가 보고되어 있다28-31). 최 등11)의 급성기 대상포진의 침구치료에 대한 해외 무작위배정임상연구 분석에서도 아시혈 다음으로 LI11(曲池), LR3(太衝), ST36(足三里)의 혈위가 많이 사용되어 본 연구와 유사한 결과를 보였는데, 발진을 비롯한 급성기 염증과 통증의 조절을 목표로 선혈한 것으로 유추해 볼 수 있다.
한약 처방으로는 龍膽瀉肝湯이 모든 분류의 대상포진에서 사용되며 10례로 가장 많이 사용되었다. 龍膽瀉肝湯은 李東垣의 《東垣十書·蘭室秘藏》에 처음 기재된 처방으로 淸瀉肝火, 淸裏濕熱하는 효능을 가져 陰部痒痛, 脇痛耳聾 등 肝膽濕熱로 인한 제반 증상에 사용되며, 《醫宗金鑑·外科心法要訣》을 비롯한 역대 한의서에서 대상포진의 치료 처방으로 가장 많이 언급되는 처방이다32,33). 실험연구를 통해 항바이러스 효능34) 및 세포성 면역 조절효과35), 항알레르기 · 항염효능36) 등이 보고된 바 있으며 이러한 효능이 대상포진의 급성 염증 반응을 완화하여 통증과 발진을 조절하는 것으로 생각된다. 최근 Wang 등의 체계적 문헌 고찰37)에 의하면 龍膽瀉肝湯은 고식적 양약치료에 비해 대상포진 급성기 통증의 기간을 단축시켰고, PHN의 발생률을 유의하게 낮춰 급성기 대상포진의 치료 목표4)에 적합한 처방이라 할 수 있다. Ramsay Hunt syndrome에서는 理氣祛風散이 더 많이 사용되었는데, 理氣祛風散은 《古今醫鑑》에서 中風, 口眼喎斜를 치료하는 것으로 수재된 이래 Ramsay Hunt syndrome을 포함한 안면마비에 다빈도로 사용되는 처방으로38,39) 육안으로 확인 가능한 후유증을 감소시키기 위해 안면마비의 치료에 더 집중한 처방을 사용한 것으로 생각된다. 또한 이 등40)은 실험연구를 통해 理氣祛風散이 신경병리성 통증을 유의하게 억제할 수 있음을 확인하였는데, 이는 신경성 통증을 동반하는 Ramsay Hunt syndrome에 더욱 효과적으로 작용할 가능성을 시사한다.
치료를 위해 사용된 본초(君藥)로는 龍膽, 柴胡가 각 8회, 澤瀉가 7회로 많이 사용되었다. 龍膽과 柴胡는 모두 肝膽經에 작용하는 약물로 龍膽은 淸熱燥濕하며 瀉肝膽火하여 수포성 발진에, 柴胡는 疏肝하여 급성기 통증 조절을 위해 重用되었음을 알 수 있다. 澤瀉는 淸熱利濕하여 龍膽瀉肝湯에서는 龍膽의 작용을 보조하기위한 佐藥으로 사용되며 君藥으로 사용시에도 龍膽과 마찬가지로 수포성 발진이 심할 경우에 사용된 것으로 보인다.
전체 구성 약재에서는 甘草(30회), 茯苓(24회), 黃芩(23회), 當歸, 生地黃(각 21회), 防風, 柴胡(각 15회)가 15회 이상 사용되었는데, 龍膽瀉肝湯을 구성하는 본초가 대부분이었고 본초학의 분류에 따라서는 解表藥, 補益藥, 淸熱藥이 각 2종, 利水滲濕藥이 1종이었다. 언급된 처방을 구성하는 모든 약재를 분류시에도 解表藥(20종), 補益藥(19종), 淸熱藥(18종), 利水滲濕藥(10종)이 다빈도로 사용되었는데, 이는 면역 저하상태와 감염으로 인한 피부의 염증성 수포 발진을 효과적으로 치료하기 위한 조합이라고 생각해 볼 수 있다.
대상포진의 임상 분류에 따라서는 범발성 대상포진에서 柴胡, 龍膽, 澤瀉가 각 5회로 가장 많이 사용되어 전체 양상과 유사한 경향을 보였고 안면대상포진에서는 柴胡(2회), Ramsay Hunt syndrome에서는 葛根(4회)이 많이 사용되었다. 葛根은 陽明經의 要藥으로 透疹·解肌하므로 안면마비를 동반하는 Ramsay Hunt syndrome에서 君藥으로 많이 쓰인 것으로 생각된다. 전체 사용 본초를 대상으로 분석 시에는 甘草, 茯苓, 黃芩, 當歸가 세 임상분류 모두에서 공통적으로 많이 사용되었고(상위 10%), 범발성 대상포진과 안면 대상포진에서는 生地黃, 梔子가, 안면 대상포진과 Ramsay Hunt syndrome에서 川芎이 공통적으로 많이 사용되었다. 범발성 대상포진과 안면 대상포진에서는 이성 대상포진(Ramsay Hunt syndrome)에 비해 비교적 발진의 범위가 넓은 경향이 있어 淸熱藥을 더하였고, 川芎은 肝膽經의 上行性 引經藥으로 祛風止痛, 活血行氣하므로 頭面部의 발진과 통증을 다스리기 위해 안면 대상포진과 Ramsay Hunt syndrome에서 多用된 것으로 보인다. 또한 범발성 대상포진에서는 澤瀉, 車前子, 龍膽, 生薑, 石膏가, Ramsay Hunt syndrome에서는 羌活, 白芷, 防風, 柴胡, 萊菔子가 각각 추가적으로 상위 빈도를 차지하였는데 범발성 대상포진에서는 발진 수포를 처리하는 약력을 강화하기 위하여 利水藥과 淸熱藥이, Ramsay Hunt syndrome에서는 안면마비가 동반되므로 초기의 風寒邪를 더 효과적으로 해소하기 위해 發散風寒藥이 重用된 것으로 생각해 볼 수 있다.
본 연구의 한계점은 검색과정에서 누락된 연구가 존재할 가능성이 있으며, 연구 대상 논문 수가 적고 그 증례 수도 논문 당 1~4례로 적다는 점이다. 또한 한약, 침, 부항 등 여러 가지 치료가 병행되어 어떤 치료가 주 효과를 발휘하였는지 파악하기 어려웠으며, 한약 처방의 명칭만 기재되어 있는 경우 약재 분석에서 누락되었다. 치료 효과에 대한 평가의 경우 평가도구가 통일되지 않았으며, 특히 피부 병변은 육안적 평가에 그쳐 치료 효과 판정에 객관성이 부족하였다. 또 대상포진 치료의 경우 PHN을 비롯한 후유증의 발생 여부가 치료 효과를 판정하는데 중요한데, 전체 33편 중 6편에서만 치료 후 추적관찰을 시행하여 전반적으로 치료 효과 판단에 대한 근거가 미비하였다. 다만 본 연구는 국내 한의학 증례 논문을 통해 대상포진의 급성기 치료 현황을 종합적으로 분석한 최초의 연구이다. 기존에 최 등11)의 급성기 대상포진 침구 치료에 대한 해외 무작위배정임상연구 분석이나 조41) 등의 대상포진 임상논문에 사용된 약침에 관한 고찰은 있었으나 한약과 침구 치료, 기타 병행 치료 등을 종합적으로 분석한 연구는 부재하였기에 의의가 있으며, 실제 임상에서의 치료 경향을 제시하였기에 향후 임상에서의 급성기 대상포진 진료에 도움이 될 수 있을 것으로 생각된다.
Ⅴ. 결 론
2019년 12월까지 대상포진의 급성기 치료와 관련된 논문을 국내 데이터베이스(OASIS, KTKP, RISS, NDSL, KISS)에서 검색하여 다음과 같은 결론을 얻었다.
-
연구 대상 논문은 33편으로 총 44건의 증례가 수집되었으며, 대상포진의 유형은 Ramsay Hunt 증후군이 20건으로 가장 많았고, 범발성 대상포진이 16건, 안면부 대상포진은 8건이었다.
-
대상포진의 급성기 치료를 위하여 가장 많이 사용된 치료법은 침(93.2%)과 한약(88.6%)이었다.
-
대상포진의 치료를 위해 총 65개의 혈위가 사용되었으며, 모든 임상 유형에서 사용된 혈위는 LI4(合谷), LR3(太衝), ST36(足三里), GB20(風池)가 있었다.
-
한약처방이 사용된 39명의 전체 증례에서 총 35개의 처방이 사용되었으며, 龍膽瀉肝湯이 10회로 가장 많이 사용되었으며 그 다음으로 理氣祛風散이 많이 처방되었는데, 理氣祛風散은 모두 Ramsay Hunt syndrome의 증례에서 사용되었다.
-
총 39개의 처방에서 115개의 본초가 사용되었는데 君藥에 해당하는 약물로는 龍膽, 柴胡, 澤瀉가 많이 사용되었다.
-
치료의 평가는 대부분 피부병변의 육안적 평가와 통증평가 도구(VAS, NRS 등)를 통해 이뤄졌으며, 안면마비의 경우에는 HB grade를 다빈도로 사용하였다.